* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 6 Review ppt
David Ricardo wikipedia , lookup
Periphery countries wikipedia , lookup
Semi-periphery countries wikipedia , lookup
Heckscher–Ohlin model wikipedia , lookup
International factor movements wikipedia , lookup
Economic globalization wikipedia , lookup
World-systems theory wikipedia , lookup
Development economics wikipedia , lookup
Internationalization wikipedia , lookup
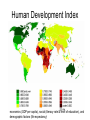
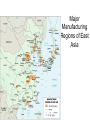
Unit 6: Economic Geo Review Human Development Index economics (GDP per capita), social (literacy rate & level of education), and demographic factors (life expectancy) Motor Vehicles per Capita Industrial Regions • Industrial Rev. began in England Major Manufacturing Regions of East Asia Balanced Growth • through Self-Sufficiency • A country should spread investment as equally as possible across all sectors of its economy and in all regions. – Incomes in rural areas keep pace with urban incomes – Businesses remain independent of foreign corporations – Limit imports through tariffs and quotas • Liberal Models by definition – Rostow’s Model – All countries are capable of development – All countries follow the same model of development • For countries that have developed in modern times – only China has followed THE model of development – Economic disparities are a result of short term inefficiencies in local or regional market forces International Trade Approach • Some countries have switched from selfsufficiency approach to international trade International Trade Approach • World Trade Organization (1995) works to reduce barriers to international trade by – Negotiate reductions in trade restrictions, such as quotas & tariffs – Enforces trade agreements IMF: • Lends to countries with balance of payments problems • Pushes for economic reforms • Reports on policies in member states World Bank: • Aims to help development by advising and lending – with many conditions • Countries encouraged to lift import and export barriers, cut subsidies and remove price controls Models of Development • Structuralist Models – Dependency Theory – Regional disparities are a structural feature of the global economy • Neo-Colonialism – Things have come to be organized or structured in a certain way and cannot be changed easily – Old method of industrializing is no longer possible because other factors have changed Wallerstein’s World Systems Theory Core Periphery Processes that incorporate higher levels of education, higher salaries, and more technology * Generate more wealth in the world economy Processes that incorporate lower levels of education, lower salaries, and less technology * Generate less wealth in the world economy Semi-periphery Places where core and periphery processes are both occurring. Places that are exploited by the core but then exploit the periphery. * Serves as a buffer between core and periphery Four Dragons • Aka Four Tigers or Gang of Four • S. Korea, Singapore, Taiwan, and Hong Kong • Lacked natural resources • Strongly influenced by Japan’s success • Concentrated on handful of manufactured goods • Low labor costs • Entrepot - sell to MDCs Millennium Development Goals • Adopted by world leaders in the year 2000 and set to be achieved by 2015, the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) provide concrete, numerical benchmarks for tackling extreme poverty in its many dimensions. The MDGs also provide a framework for the entire international community to work together towards a common end – making sure that human development reaches everyone, everywhere. If these goals are achieved, world poverty will be cut by half, tens of millions of lives will be saved, and billions more people will have the opportunity to benefit from the global economy. Millennium Development Goals The eight MDGs break down into 21 quantifiable targets that are measured by 60 indicators. • • • • • • • • Goal 1: Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger Goal 2: Achieve universal primary education Goal 3: Promote gender equality and empower women Goal 4: Reduce child mortality Goal 5: Improve maternal health Goal 6: Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases Goal 7: Ensure environmental sustainability Goal 8: Develop a Global Partnership for Development http://www.undp.org/mdg/basics.shtml • All industries want to maximize profits by minimizing costs so if choose locations based on – Energy – Labor – Transportation – Or Footloose Location Models Weber’s Model Manufacturing plants will locate where costs are Hotelling’s Model the least (least cost Location of an industry theory) cannot be understood Theory: without reference to other industries of the Least Cost Theory same kind. Costs: Transportation, Theory: Labor, Agglomeration Locational interdependence Losch’s Model Manufacturing plants choose locations where they can maximize profit. Theory: Zone of Profitability Least Cost Theory Alfred Weber’s model – owners of manufacturing plants seek to minimize costs through: • • • 1) Transportation, and 2) labor 3) agglomeration – Weight-losing / weight-gaining Hotelling’s Model • Harold Hotelling (1895-1973) • Locational Interdependence • Originally locate near customers – but will gravitate to each other to maximize profits • The costs for some customers will be greater if the 2 sellers cluster – further to walk. Also fewer customers aware of service. But can’t move for fear of losing customers. Changing Markets • Outsourcing • New international division of labor – Moving industry to low-cost labor • Just-in-time Delivery • Post-Fordist system – more flexible, less mass produced (time-space compression) • deindustrialization • • • • Break of bulk points Informal economy High-tech corridors agglomeration