* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Planned economy
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
Participatory economics wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Economic planning wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Criticisms of socialism wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Money supply wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
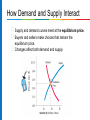
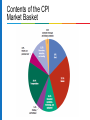
Chapter 3 Economic Challenges Facing Contemporary Business Learning Objectives LO 3.1 Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics. Explain the factors that drive demand and supply. LO 3.2 Describe the four types of market structures in a private enterprise system, and compare the three major types of economic systems. LO 3.3 Identify and describe the four stages of the business cycle. Explain how productivity, price level changes, and employment levels affect the stability of a nation’s economy. LO 3.4 Discuss how monetary policy and fiscal policy are used to manage an economy’s performance. LO 3.5 Describe the major global economic challenges of the 21st century. Economics The social science that studies the choices people and governments make when dividing up their scarce resources Demand: The willingness and ability of buyers to purchase goods and services Supply: The willingness and ability of sellers to provide goods and services Test Your Knowledge Economics is the study of a. the choices people and governments make when allocating scarce resources. b. profit and loss at companies. c. tax and interest policies. d. demand and supply. Test Your Knowledge Economics is the study of a. the choices people and governments make when allocating scarce resources. b. profit and loss at companies. c. tax and interest policies. d. supply and demand. Answer: A Microeconomics The Forces of Demand and Supply The study of small economic units, such as individual consumers, families, and businesses Factors Driving Demand Demand curve: A graph of the amount of a product that buyers will purchase at different prices Driven by variety of factors such as competition, price, larger economic events, and consumer preferences Demand Curve A graph of the amount of a product that buyers will purchase at different prices Factors Driving Supply Factors of production play a central role in the overall supply of goods and services A change in the cost or availability of any of these inputs can shift the entire supply curves and services. Supply Curve A graph that shows the relationship between different prices and the amount of goods that sellers will offer for sale, regardless of demand How Demand and Supply Interact Supply and demand curves meet at the equilibrium price. Buyers and sellers make choices that restore the equilibrium price. Changes affect both demand and supply. Macroeconomics Issues for the Entire Society Political, social, and legal conditions differ in every country. Economies generally classified in one of three categories: Private enterprise system (capitalism or market economy) Planned economies: socialism, communism Mixed market economies (combinations of the two) Capitalism The Private Enterprise System and Competition Businesses meet needs and demands of consumers and are rewarded through profit. Government favours a hands-off approach. Marketplace competition regulates economic life. Four degrees of competition: Pure competition Monopolistic competition Oligopoly Monopoly Types of Competition Test Your Knowledge The market structure that is most likely to be regulated is a. b. c. d. pure competition. monopolistic competition. oligopoly. monopoly. Test Your Knowledge The market structure that is most likely to be regulated is a. b. c. d. pure competition. monopolistic competition. oligopoly. monopoly. Answer: D Planned Economies Planned economy: An economic system where business ownership, profits, and resource allocation are shaped by a plan to meet government goals Socialism Communism An economic system where the government owns and operates the major industries, such as communications Some private ownership of industry allowed, such as retail and some manufacturing An economic system where all property is shared equally by the people in a community under the direction of a strong central government Adopted in early 20th century by many nations, but governmentowned monopolies often suffered from inefficiency Mixed Market Economies Mixed market economy: an economic system that draws from both private enterprise economies and planned economies, to different degrees The mixture of public and private enterprise can vary widely from country to country. Privatization: The conversion of governmentowned and -operated companies to privately-held businesses Comparison of Alternative Economic Systems Evaluating Economic Performance An economic system should provide a stable business environment and sustained growth as benefits for its citizens. Business decisions and consumer behaviour differ at various stages of the business cycle: Prosperity—Unemployment low, consumer confidence/purchasing high, businesses expanding Recession—A cycle of economic contraction that lasts for six months or longer; consumers careful about purchases, businesses slow production/expansion Depression—Extended recession Recovery—Declining unemployment, increasing business activity, renewed consumer confidence Productivity and the Nation’s Gross Domestic Product Productivity: The relationship between the number of units produced and the number of human and other production inputs needed to produce them Gross domestic product (GDP): The sum of all goods and services produced within a country during a specific time period, such as a year The Canadian GDP is tracked by Statistics Canada Test Your Knowledge If labour hours increase, the use of natural resources remains the same, and output remains the same, productivity a. will increase. b. will remain the same. c. will decrease. d. cannot be determined. Test Your Knowledge If labour hours increase, the use of natural resources remains the same, and output remains the same, productivity a. will increase. b. will remain the same. c. will decrease. d. cannot be determined. Answer: C Price-Level Changes Inflation: Rising prices caused by a combination of excessive consumer demand and higher costs of raw materials, component parts, human resources, and other factors of production Core inflation rate: The inflation rate after energy prices and food prices are removed Demand-pull inflation: Excessive consumer demand Cost-push inflation: Increases in costs of the factors of production Hyperinflation: An economic situation marked by soaring prices Inflation devalues money. People can purchase less with what they have (decreased purchasing power). Deflation: The opposite of inflation, occurs when prices continue to fall Can cause a weakened economy Measuring Price-Level Changes Changing prices are tracked by the Consumer Price Index (CPI). A measurement of the monthly average change in prices of goods and services Commonly purchased goods and services are priced to compile the data included in the CPI “market basket” See the Bank of Canada site for the CPI from 2000 to present. Contents of the CPI Market Basket Employment Levels Unemployment rate: The percentage of total workforce actively seeking work but currently unemployed Four types of unemployment: Statistics Canada Labour Force Survey Managing the Economy’s Performance Monetary policy: A government plan to increase or decrease the money supply and to change banking requirements and interest rates to affect bankers’ willingness to make loans Expansionary monetary policy: A plan to increase the money supply to try to decrease the costs of borrowing Lower interest rates encourage new investments and increases employment and economic growth. Restrictive monetary policy: A plan to decrease the money supply to control rising prices, overexpansion, and concerns about overly rapid economic growth The Bank of Canada formulates and implements monetary policy. Government uses monetary and fiscal policy to fight unemployment, Fiscal Policy Fiscal policy: A plan of government spending and taxation decisions designed to control inflation, reduce unemployment, improve the general welfare of citizens, and encourage economic growth The federal budget is an annual plan for how the government will raise and spend money in the coming year. The primary sources of government funds are taxes, fees, and borrowing. When the government spends more than the amount of money it raised, there is a budget deficit. When we borrow money to cover the deficit, the national debt is increased. If the government has more money than it spends, there is a budget surplus. Global Economic Challenges