* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Criticisms of socialism wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
Long Depression wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
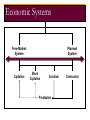
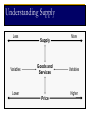
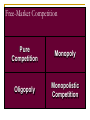
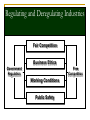
BA 101 Introduction to Business 1. Fundamentals of Business and Economics What is a Business? Knowledge Non-Profit • Goods • Education • Services • Libraries • Job creation • Museums • Tax-base • Social services • Investments • Charities Entrepreneurs Capital Resources For-Profit Categories of Business Producing Goods Capital Intensive Providing Services Labor Intensive Service Sector Growth More disposable income Lifestyle and demographic changes Complex goods and technologies Need for professional advice Low barriers to entry What is Economics? Microeconomics Macroeconomics Economic System Factors of Production Resources Capital Entrepreneurs Knowledge Economic Systems Free-Market System Capitalism Planned System Mixed Capitalism Socialism Privatization Communism Microeconomics The Forces of Supply and Demand Supply and Demand Supply: Specific quantity of a product that the seller is able and willing to provide Demand: Buyers’ willingness and ability to purchase products Consumer Preferences Price of Substitute Products Price of Complementary Goods Demand Advertising and Promotion Spending Expectations About Future Prices Higher Lower Price Consumer Income Lower Higher Understanding Demand Understanding Supply Less Variables Lower Supply Goods and Services Price More Variables Higher The Relationship between Supply and Demand Variables that affect supply and demand change simultaneously and continually, thus creating changes in the equilibrium price. Both production levels and prices reflect the interaction of supply and demand. Macroeconomics Issues for the Entire Economy Free-Market Competition Pure Competition Monopoly Oligopoly Monopolistic Competition Competitive Advantage Price Speed Quality Service Innovation The Role of Government Fostering competition Regulating industries Deregulating industries Protecting stakeholders’ rights Contributing to economic stability Fostering Competition Antitrust Legislation Mergers and Acquisitions Regulating and Deregulating Industries Fair Competition Business Ethics Government Regulation Free Competition Working Conditions Public Safety Contributing to Economic Stability Economic Expansion Recovery Fiscal Policy Business Cycle Business Cycle Monetary Policy Recession Revenue and Spending Economic Contraction Interest Rates Major Economic Indicators Housing Starts Durable-Goods Orders Interest Rates Unemployment Statistics Measuring Price Changes Inflation Purchasing Power Consumer Price Index (CPI) Deflation Measuring National Output Dollar Value Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Gross National Product (GNP) Final Goods and Services Yes Yes Domestic Businesses Yes Yes Foreign-Owned Businesses Yes No Overseas Operations No Yes Ten Economic Performance Indicators Prime Interest Rate Unemployment Rate Housing Starts Durable-Goods Orders Labor Productivity Rate Balance of Trade Rate of Inflation Producer Price Index Consumer Price Index Gross Domestic Product What does the future hold? The aspect of terrorism China in the global economy Work mobility Deficits in budget and balance of trade E-business Challenges of Globalization Quality products and services Changing needs of customers Managing a small business Globalization and workforce diversity Ethics and social responsibility Technology and electronic commerce