* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Geography By James Rubenstein
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
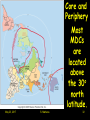
Human Geography By James Rubenstein Chapter 9 Key Issue 4 Why Do Less Developed Countries Face Obstacles to Development? May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 1 In recent years, LDCs have made improvements in development, but the gap between LDCs and MDCs have continued to widen. Natural Increase has dropped 20% in LDCs compared to 83% in MDCs. 1/5th of the world’s people (in MDCs) consume 5/6ths of the world’s goods. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 2 Progress toward development May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 3 To reduce disparities between the rich and poor countries, LDCs must develop more rapidly. They must . . . adopt policies that successfully promote development (emphasis is on international trade). They must find funds to pay for the development (emphasis is on self-sufficiency). May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 4 Elements of SelfSufficiency Approach 1. Spread investment as equally as possible across all sectors of the economy and regions. 2. Isolate fledgling businesses from international corporations. 3. Set barriers to limit imports. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 5 India: Example of the Self-Sufficiency Approach 1. Limited imports of foreign goods 2. Exports were discouraged. 3. Government approval required for expansion. 4. Businesses subsidized. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 6 Problems with the SelfSufficiency Alternative 1. Inefficiency - protects inefficient businesses. 2. Large Bureaucracy – the complex administration, needed to manage controls, encouraged abuse and corruption. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 7 Elements of International Trade Approach 1. What resources does a country have in abundance that other countries are willing to buy? 2. What products can the country manufacture and distribute at a higher quality and lower cost to other countries? May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 8 *Rostow’s 5 stage Development Model 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The The The The The May 23, 2017 traditional society. preconditions for takeoff. takeoff. drive to maturity. age of mass consumption. S. Mathews 9 The Traditional Society A very high percentage of population engaged in agriculture. A high percentage of national wealth allocated to “nonproductive” activities, such as the military and religion. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 10 The Preconditions for Takeoff Under influence of well educated leaders, the country starts to invest in new technology and infrastructure, such as water supplies and transportation systems. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 11 The Takeoff Rapid growth, technical advances, and high productivity occur in a limited number of economic activities. Other sectors of the economy remain dominated by traditional practices. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 12 The Drive to Maturity Modern technology diffuses from take-off industries to a wide variety of industries. Workers become more skilled and specialized. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 13 The Age of Mass Consumption The economy shifts from production of heavy industry to consumer goods. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 14 MDCs are in stages 4 and 5. As a country concentrates on international trade, it benefits from exposure to consumers in other countries. Rostow’s model suggests that any country can become more developed. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 15 Examples of International Trade Approach Persian Gulf States used petroleum revenues to finance large projects and provide consumers goods. South Korea, Singapore, Taiwan, and Hong Kong used cheap labor to produce and sell products inexpensively. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 16 Problems with the International Trade . Alternative May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 17 Problems with the International Trade Alternative 1. Uneven Resource Distribution 2. Market Stagnation 3. Increased Dependence on MDCs May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 18 Uneven Resource Distribution LDCs suffer when the resource that they have for sale doesn’t command a large enough price to enable them to purchase products needed for growth. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 19 Market Stagnation The slow growth of MDCs population can and has limited market size of products from LDCs. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 20 Increased Dependence on MDCs Investments in takeoff industries may reduce production of necessities for the population, forcing an LDC to depend on MDCs for those necessities. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 21 Recent Triumph of the International Trade Approach Since India dismantled its barriers to international trade, its per capita GDP has increase from 4% to 6% annually. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 22 World Trade Organization Established in 1995, by countries representing 97% of world trade, to promote, and remove barriers to international trade in all countries. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 23 Critics of the WTO Liberals charge the WTO as antidemocratic. Conservatives charge that the WTO compromises the sovereignty of individual countries. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 24 Financing Development LDCs must generally obtain loans from MDCs. From banks and international organizations, and From direct investment by transnational corporations. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 25 Loans The World Bank and the International Monetary Fund lend about $50 billion annually to LDCs for development. Commercial banks from MDCs have a current outstanding loans to LDCs totaling $2.1 trillion. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 26 Problems with Loans Half of the projects funded in Africa have ended up as failures. Many LDCs have accumulated debt that exceeds annual income. Lending agencies have had to cancel debt and encouraged LDCs to adopt structural adjustment programs. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 27 Debt as a percentage of income May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 28 Structural Adjustment Programs Policies that create conditions encouraging international trade, such as raising taxes, reducing government spending, controlling inflation, selling publicly owned utilities to private corporations, and charging citizens more for services. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 29 Transnational Corporations Corporations operating in countries other than the one in which its headquarters are located. May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 30 Flow of Investment May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 31 Core and Periphery Core and Periphery Most MDCs May 23, 2017 S. Mathews Most MDCs are located above the 30o north latitude. 32 Finis May 23, 2017 S. Mathews 33