* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What`s going on? Where, why, and to whom? March 2003 Adrian Orr
Survey
Document related concepts
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Long Depression wikipedia , lookup
Economic calculation problem wikipedia , lookup
Uneven and combined development wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
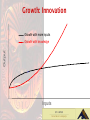
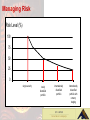
Young Maori Leaders Conference Economic Resources Temuera Hall 17 June 2003 Why Economic Growth? Growth increases choice – – – – health education welfare cultural security What Generates Economic Growth? The Human Element • People – how many? – how smart? – how motivated? • Resources - land and capital • Decreasing returns to scale What creates economic growth? • More inputs (labour and capital) • Same things better - productivity • Better things - innovation Entrepreneur + Innovator = Growth Growth: Innovation Growth with more inputs Output Growth with knowledge Inputs Same things better and better things 4000 3500 3000 Commodity Price Index New Zealand GDP US GDP Revolution? 2500 2000 1500 Evolution 1000 500 0 Mar-60 Mar-65 Mar-70 Mar-75 Mar-80 Mar-85 Mar-90 Mar-95 Mar-00 Generating Economic Growth Economic growth Productivity Labour quality Capital quality Individual incentives Macroeconomic stability Property rights & Governance Labour Capital Natural resources/ geography 22 Bold leaps forward Take-off 6 GDP per person in Western Europe, $’000, 1990 prices Mechanisation in farming; steam engines; Arkwright’s spinning machine (1769); Crompton’s mule (1779); bridge at Coalbrookdale, England, first structural use of cast iron (1779) Padded horse collar (around 1100); first recorded windmall with vertical sails rotating about horizontal axis (1185) Domesday Book shows 5,624 watermills in England south of the Severn Volta’s electric battery (1800); electromagnetic telegraph (1833); first transatlantic telegraph cable (1858); Bell’s telephone (1876); Edison’s carbon-filament lamp (1878); Marconi’s wireless patent (1896) 4 First telescopes; Huygens invents pendulum clock (1658) Gutenberg’s printing press Invention and development of compass; year-round navigation in Mediterranean after 1250 Advances in large-scale hydraulic engineering; Languedoc Canal joins Atlantic and Mediterranean (1681) Blast furnace Bessemer and Siemens-Martin 2 (open-hearth) processes for making steel Car powered by internalcombustion engine (1885); Henry Ford’s Model T 0 (1908) Powered flight (1903) 1 1000 1050 1100 1150 1200 1250 1300 1350 Source: Angus Maddison 1400 1450 1500 1550 1600 1650 1700 1750 1800 1850 1900 1950 2000 The growth process Knowledge Experience SERVICE PROCESS GROW DIG It’s a small world • Globalisation: capital and labour free to move • Decisions made and judged on a global basis • Access to all investors and investments • Diversify or die!! CURRENT MAORI ECONOMY Agriculture 60% Forestry 10% Fishing 12% Other 18% Total 100% 82% Typical Risks • Exchange rate • Commodity prices (price taker) • Nature (primary based) • Governance (property rights) • Skills (education) • Market and products (Doha round) • Regulatory changes (Kyoto, GE, RMA..) Barriers to Maori economic growth? • • • • • • • Education attainment - skills Location Assets Property rights Governance Aggregation • Natural Resources - rain, grass, ocean The will…? • Geography - isolated, small • Capital, Labour - average Maori Business Issues •Common Issues: – – – – – Governance Management Accountability Transparency Communications In Short: Generic business issue Systems & Processes commercial knowledge and experience Role of education Education – makes individual workers more productive - direct; – leads to the creation of knowledge - indirect. Role of education • “…the improvement in human capital seems to be a common factor behind the growth in recent decades in all OECD countries…. the increase in human capital accounted for more than half an extra percentage point of growth in the 1990s compared with the previous decade” OECD, 2001 Maori Economic Vulnerability • • • • Narrow asset base - farm, forestry Commodity price-takers All assets in New Zealand Capital constraints Generating Economic Growth • • • • • • Property rights - Collective Ownership Agreement on asset use Governance : creation or distribution? Individual incentives and accountability Fixed assets Access to credit Generating Economic Growth Individual Incentives • • • • • Education - relative wages, opportunities Work effort - tax, welfare Openness - trade, ideas, people Regulatory environment - investment Saving and investment Basic Investment Concepts Risk vs Return Growth / Income Capital Protection Liquidity Asset Allocation Time Horizon Managing Risk Risk Level (%) 100 75 50 25 0 0 single 1 security 2 locally diversified portfolio internationally 3 diversified portfolio internationally 4 diversified portfolio with currency hedging Economic Resources Active Passive Structure Outputs Goals Values Do we need a Maori Bank? Business Basics • Business must make a profit • Profit to exceed lending rates • Cashflow priority • Comply with regulations • Know & manage risk • Global Marae Business Basics • Every industry sector has a benchmark • Doing things right (governance & mgmt) • Making a difference – People / ideas / experience • System and process • Supply & Demand Business Reality • A good profitable Business: – Exclusive industry niche – Technology break through – Exceptional efficiency – Market dominance /scale – Sustainable Top 10% Maori Business Reality • Value base – Cultural values (kauwae runga) – Uniqueness / character (kauwae raro) Te Tahuhu Te Mauri • Key drivers – Commercial – Social / environmental – Cultural Te Ihi me te Wana • Achievable outcomes – Realistic expectations – Know your cashflow – Identify & manage risk Te wero me te hua LTF - Investment Planning Goals & Objectives Analyse Investment Needs Risk Profile Investment Parameters Performance Monitoring Investment Planning Process Process: Understand current asset portfolio Determine current & potential income streams Identify core business Identify current risks Determine income requirements Determine investment objectives Develop risk profile