* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download American Dilemmas - St. Edward's University
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Protectionism wikipedia , lookup
American School (economics) wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Italy under fascism wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
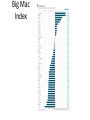
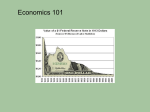
ECONOMICS 1/31/2012 Learning Objectives • • Critically analyze social problems by identifying value perspectives and applying concepts of sociology, political science, and economics; Use knowledge and analyses of social problems to evaluate public policy, and to suggest policy alternatives, with special reference to questions of social justice, the common good, and public and individual responsibility. Opportunities to discuss course content • Today- 12:00-2:00 • Wednesday- 11-2:00 Readings • Required – Economic Policy (Chapter 7) Dye – American Dilemmas Handbook, pp 73-88 • Optional – Wealth and Poverty: U.S. and Global Economic Inequalities (Chapter 2) Kendall Paper Proposal • Due in class on 2/7 • 5% of your final Grade • Involves submitting 2 Parts – Worksheet – 2 page paper Economics The Dismal Science Economics • Fiscal Policy • Monetary Policy The Economy as a series of sectors The Modern U.S. Economy • A Shift Away from the First Two Sectors • A Service Based Economy – Affluent service jobs – Welfare service – Service Jobs The Economy as a series of “Collar” Jobs • • • • White Collar Blue Collar Pink Collar Green Collar Collar does not always equate with income Who Does it ECONOMIC POLICY MAKERS Key actors in Economic Policy • We do not have a single economic policy • The federal government is the key player here, why? – The Power to Tax – Regulate foreign trade – Coin Money and set its value States and municipalities are also Big Players • They can also tax • They can provide incentives for economic growth • Provide services for its residents Economic Growth: Goal #1 • An Increase in the GDP each year • More Money means more tax revenue • uncontrolled growth, however, is not a good thing Historical GDP Change Low Unemployment: Goal 2 • What is Unemployment • Who does this Exclude? • What it doesn’t measure? The Positive aspects of Low Unemployment • More Tax Revenue • Fewer people receiving benefits • Lower Crime Unemployment in U.S. Our Unemployment compared to other Nations • Historically, it has been much lower • Even in our poor economy, it is lower than the EU region The Decline of Labor Unions The Economic and Political Effect of Unions • Union Workers earn 10% to 15% than nonunion workers in similar occupations • A large player in “special interest” politics Why the decline in Organized Labor • The Growth in “RTW” States • The decline in manufacturing jobs and large factories • Globalization of the economy • Government has assumed many of labor’s roles Economic Goal 3: Low Inflation • What causes inflation? • The Government wants low levels of inflation, why? The Consumer Price Index • What it includes • What it excludes • How it has changed over time Goal 4: A positive Balance of Trade • A Nation Wants to Export more than it Imports • The United States is the reverse The Big Mac Index • A way of measuring the strength of the dollar • Big Mac’s involve a fixed product • What it involves • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sz656YOEixI Big Mac Index Our Trade Deficit Why We have a Trade deficit • Where it comes from • What are the reasons The Advantages and Disadvantages of a Trade Deficit • Disadvantages • Advantages