* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Financial crisis of 2007–2008 wikipedia , lookup
Fixed exchange-rate system wikipedia , lookup
Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission wikipedia , lookup
Exchange rate wikipedia , lookup
Financial crisis wikipedia , lookup
International monetary systems wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
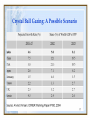
Macroeconomic Policy Challenges for India By Dr. Shankar Acharya Macroeconomic Policy Challenges for India • • • • • Foreign Capital Surge of 1993/94 Asian Financial Crisis of 1997/98 Fifth Pay Commission The Employment Challenge Economic Growth: Past, Present and Future. Foreign Capital Surge of 1993/94 • Event: $12 billion (4% of GDP) added to foreign exchange reserve between sept.1993 and oct. 1994. • 3 Major Policy Issues 1. Should nominal exchanges rate be allowed to appreciate (text book)? How to transform “problem” of capital surge into opportunities for liberalizing external trade and payments. If reserves were going up sharply, what could authorities do to limit impact on inflation? 2. 3. • Policy Choices Mode 1. Build-up RBI’s reserves and prevent nominal appreciation of rupee Undertake number of payments liberalization measures Undertake partial “Sterilization” of foreign asset accumulation. 2. 3. Asian Financial Crisis (1) Lessons 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Avoid high levels of short-term external debt Avoid sustained and substantial appreciation of country’s real effective exchange rate (REER) Avoid massive drawdown of foreign exchange reserves in vain attempt to defend unrealistic exchange rate Strengthen domestic financial sector, especially banks (capital adequacy, prudential norms, etc) Prudential limit for exposure of banks to speculative markets (stocks, real estates). Keep current account deficit of BOP at manageable levels. Cautious approach to Capital Account Convertibility. Asian Financial Crisis (2) What India Did 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Short–term debt under tight control after 1991 crisis. Market determined exchange rate managed judiciously in 1993-97. Rupee allowed to depreciate by 16% in “stress period” AugustDecember 1997. Some use of foreign exchange reserves to put brakes on depreciation, Substantial banking reforms in period 1992-97. Bank exposure to stock and real estate markets limited by norms. Current account deficit contained after 1991 crisis. Cautions approach to Capital Account Convertibility. Monetary policy tightened in January 1998. Fifth Pay Commission Pay and Pensions of Employees of Central and State Governments 1993/94 1994/95 1995/96 1996/97 1997/98 1998/99 1999/2000 Rs. Crores Pay and Pensions 48323 54111 63710 73432 89748 111891 133381 (of which pensions) (8445) (9789) (12090) (14921) (18480) (26223) (36581) As Percent of GDP Pay and Pensions 5.6 5.3 5.4 5.4 5.9 6.4 6.9 (of which pensions) (1.0) (1.0) (1.0) (1.1) (1.2) (1.5) (1.9) Revenue Deficit 4.3 3.7 3.2 3.6 4.1 6.3 6.3 Fiscal Deficit 8.3 7.1 6.5 6.4 7.3 8.9 9.5 Sources: Budget documents, CSO and RBI Employment Challenges Income, Growth and Population: Major States Income, Growth and Population: Major States (Contd………………) Economic Growth: Past, Present and Future Growth rate of GDP and Major Sectors 1951/52-1980/81 1981/82-1990/91 1992/93-1996/97 1997/98-2000/1 2001/2-2005/6 GDP 3.6 5.6 6.7 5.5 6.7 Agriculture 2.5 3.6 4.7 1.0 2.5 Industry 5.3 7.1 7.6 4.8 7.0 Services 4.5 6.7 7.6 8.5 8.5 Source: CSO; data for 1951/52 to 1999/2000 are at 1993/94 prices and for 2000/01 to 2005/06 at 1999/2000 prices Growth: Recent and Outlook (%per annum) Crystal Ball Gazing: A Possible Scenario