* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download UNIT 1 - GUNS and ROSES
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Participatory economics wikipedia , lookup
Criticisms of socialism wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Uneven and combined development wikipedia , lookup
Socialist calculation debate wikipedia , lookup
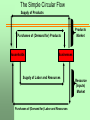
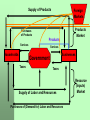
UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Economics is the study of how we can best increase a country’s wealth with the resources that we have available to us. UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Marginal Benefit is the additional satisfaction or value one obtains from an activity or product. Marginal Cost is the additional cost or sacrifice one makes of participating in an activity or purchasing a product. UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Economic Decision-Making You decide to participate in an activity (going to college, buying something, etc.) as long as your marginal benefit exceeds your marginal cost. UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Macroeconomics and Microeconomics The nation's unemployment rate, inflation, interest rate trends, government budgets, government fiscal policies, economic growth, and monetary policy, are topics discussed in _____ (fill in the blank). For inflation and unemployment rates, visit http://www.bls.gov/ UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Macroeconomics and Microeconomics Price elasticity (sensitivity) of demand for goods and services, firms’ production behavior, cost functions, income inequality, and protectionism, are topics discussed in _____ (fill in the blank). For information about income inequality among various groups, visit: http://www.census.gov UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts The Production Possibilities Curve A production possibilities curve represents outcome or production combinations that can be produced with a given amount of resources. UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts The Production Possibilities Curve GUNS 600 500 E C F B 400 G A 300 D 350 500 580 700 ROSES UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Economic Growth If an economy is operating at a point on the production possibilities curve, all resources are used, and they are utilized as efficiently as GUNS possible. 600 500 E C F B 400 G A 300 D 350 500 580 700 ROSES UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Economic Growth Is Caused by: Increases in Resources And Advances in Technology UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Your Own Personal PPC If two possible outcomes in your own personal life are job earnings and educational credits, then your PPC may look as follows: Job earnings 30000 E C 23000 F B 16000 G A 12000 D 10 18 23 30 College credits UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Three Economics Systems are: 1. Capitalism 2. Communism 3. Socialism UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Capitalism Characteristics The role of the government is limited to the most essential functions. All prices are determined in the free market (supply and demand). UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Capitalism Characteristics The role of the government is limited to the most essential functions. All prices are determined in the free market (supply and demand). UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Capitalism Characteristics The role of the government is limited to the most essential functions. All prices are determined in the free market (supply and demand). UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Communism Characteristics Government makes all decisions regarding production, prices, wages, interest rates, and income distribution. UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Socialism (Mixed Economy) Characteristics Most economic decisions are made by the private sector, but the role of the government is significant. Government spending and taxes are relatively high. Survey question. On a scale of 1through 5 (1 = most capitalist, and 5 = most communist), which economic system do you prefer? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1 2 3 4 5 UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Grading Systems Capitalist: every student gets the grade (s)he works for. Communist: all scores are added up, then divided by the number of students in the class. Everyone receives the same grade. Socialist: some points are taken from the higher scoring students and given to the lower scoring students. Survey question. On a scale of 1through 5 (1 = most capitalist, and 5 = most communist), which grading system do you prefer? 1. 1 (our current system) 2. 2 (little bit of redistribution of grades) 3. 3. (redistribution of grades) 4. 4 (significant redistribution of grades) 5. 5 (all grades equal) Survey question. Assuming we keep our current pure capitalist grading system, would you support the option of a student voluntarily giving up a letter grade to help a student with a lower grade? 1. 2. 3. 4. Yes No Indifferent Don’t know UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Economic Growth and Economic Systems Countries with the highest overall economic standard of living have the freest markets (more elements of capitalism). Examples: Hong Kong, the United States, Japan, Taiwan, Great Britain, Canada, Sweden, South Korea, and Singapore. UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts 2010 Purchasing Power Parity (unless otherwise noted) Gross Domestic Product estimated in billions of dollars, and Per Capita (person) GDP Country/Area GDP Per Cap. GDP World United States China Hong Kong Korea - North Korea - South Luxembourg Qatar $ 74,540 $ 14,660 $ 10,090 $ 326 $ 40 $ 1,459 $ 41 $ 151 $ 11,200 $ 47,200 $ 7,600 $ 45,900 $1,800 $ 30,000 $ 82,600 $ 179,000 For GDP information of other countries around the world, see our CD, Unit 3, Section 2 UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Economies around the World Most industrialized countries are mixed economies, but they also have many capitalist elements. Characteristics include Substantial activity in the private sector (businesses and households). Prices are determined by demand and supply. A significant role by federal and local governments. UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts The Role of Government Functions include: Spending on defense, roads, legal system, public services and education Redistributing incomes through taxes and subsidies Passing laws and imposing regulations Implementing price controls Conducting monetary policy to affect inflation, interest rates, and employment UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Important Concepts and Definitions We will discuss the following concepts: The simple circular flow The circular flow with government and foreign markets Nominal and real prices and incomes Positive and normative economic statement The fallacy of composition The fallacy of cause and effect The Simple Circular Flow Supply of Products Purchases of (Demand for) Products Households Products Market Businesses Supply of Labor and Resources Purchases of (Demand for) Labor and Resources Resource (Inputs) Market UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts The circular flow with government and foreign markets (see next slide). This is a more complex (more realistic) model. Supply of Products Foreign Markets Products Market Purchases of Products Products Services Households Services Businesses Government Taxes Taxes Supply of Labor and Resources Purchases of (Demand for) Labor and Resources Resource (Inputs) Market UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Nominal and Real Prices Nominal prices are expressed in current dollars. Real prices are adjusted for inflation. Enough money to purchase 3 gallons of gasoline a few years ago. Not enough to purchase 2 gallons today. UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Positive and Normative Economic Statements A positive statement can be proven or disproven. A normative statement is an opinion or value judgment. UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Which is the Normative and Which is the Positive Economic Statement? Statement I: The minimum wage should increase to $8.50. Statement II: If the minimum wage increases, then a firm’s cost of production rises. UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts The Fallacy of Composition Fallacy: what is good for one person (or one group) is good for all persons (or all groups). UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts The Fallacy of Cause and Effect Because A happens before B, A must be automatically the cause of B. UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Cause and Effect Fallacy Example A: The car industry in country X has not done well. B: The economy of country X has not done well. Did A cause B? UNIT 1 - Fundamental Concepts Critical Thinking Guidelines Question the source. Question the assumptions. Question how the variables are defined. Question the validity of the statement. Question the statistics. Think like an economist.