* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Edmund Phelps wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Full employment wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
Keynesian Revolution wikipedia , lookup
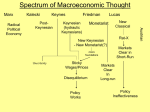
Lecture: Who is Who in Macro (Historical Excursion) Alemayehu Geda Departments of Economics University of London and Addis Ababa University May, 2006 5/23/2017 1 Macro Model and Macro Paradigms Historical 5/23/2017 Excursion 2 Historical Excursion Great Depressi on 1929 Classical Keynes 1936 Now…. Modigliani 1937 ‘43 ‘50 ’70/80 Hicks 5/23/2017 3 Macroeconomic is Concerned: Aggregates: Inflation, Output, unemployment… Action of Gov’t affects aggregates Fiscal Monetary 5/23/2017 4 Three Event for Evolution of Macro: Systemic Data Collection Business Cycle Great Depression Follows Says law Markets are self-regulating 5/23/2017 5 Keynes’ General Theory Markets are not Self-regulating Gov’t Intervention is desirable Kalecki already noted 5/23/2017 6 Neoclassical Synthesis Keynesians (NCSK) Old/Neo Keynesians is also used Many recognized the unemployment is not temporary But hold to Classical axioms Neutrality of money Gross Substitution assumption Erogodic Economic Environment Cast Keynes in Classical Set-up – The IS/LM Ad hoc Constraints are used 5/23/2017 7 New Keynesian Obey to Classical Axioms Introduce sophisticated (non-ad hoc) Constraints Coordination failure Asymmetric information Transaction/menu costs etc… If Prices are flexible and information free – coincides with classical Both old and New take the classical system as the general system and Keynes as special case 5/23/2017 8 New Classical Macroeconomics Add a strong statement that summarizes how you feel or think about this topic Summarize key points you want your audience to remember 5/23/2017 9 Post Keynesian Macroeconomics Argue that Keynes’ revolution is aborted Take Kaldor, Klaecki, Robinson and Keynes as intellectual ancestors Concerned with RECOVERY and EXTENSION of Keynes 5/23/2017 10 Fundamental basis of PK are: Role of Social Conflict in distribution of income Centrality of aggregated demand in determining output Inability of nominal wage adjustment to bring about solution to the unemployment problem Endogenous nature of money Fundamental and mutable nature of expectations 5/23/2017 11 Structural Macroeconomists Basically similar to PKs Emphasize class and distribution of income/political economy Importance of intuitions and economics structure in shaping agents behaviors The possibility of both quantity and price clearing in markets They focus on developing countries 5/23/2017 12 HETRODOX MACROECONOMICS Refers to (A) Post-Keynesian and, (B) Structuralist Macroeconomics 5/23/2017 13 (A) Post Keynesian Macroeconomics Argue that Keynes’ revolution is aborted Take Kaldor, Klaecki, Robinson and Keynes as intellectual ancestors Concerned with RECOVERY and EXTENSION of Keynes 5/23/2017 14 Fundamental basis of PK are: Role of Social Conflict in distribution of income Centrality of aggregated demand in determining output Inability of nominal wage adjustment to bring about solution to the unemployment problem Endogenous nature of money Fundamental and mutable nature of expectations 5/23/2017 15 (B) Structural Macroeconomists Basically similar to PKs Emphasize class and distribution of income/political economy Importance of intuitions and economics structure in shaping agents behaviors The possibility of both quantity and price clearing in markets They focus on developing countries 5/23/2017 16 Structural Macroeconomists (Cont’d) Building on similar ideal to PKs ‘An economy has a structure if its institutions and the behavior of its members make some patterns of resource allocation and evolution substantially more likely than others. Economic analysis is structuralist when it take these factors as the foundation stones for its theories’ Taylor 1983. 5/23/2017 17 Structuralist Cont’d The Structuralist approach embraces three premises (FitzGerald & Vos 1989): (1) Economies are built up from agents such as firms, governments & households whose who are not simple optimizers but their behavior depends on the context of institutions, production organization or social class in which they operate (2) Markers may show rigidities, perverse response to price owing to institutional behavior, market power, imperfect information and class interest (3) Institutional setting and relate market rigidities are basic structural features but are not unchangeable over time 5/23/2017 18 The Structural Approach also emphasize: The possibility of both quantity and price clearing in markets Income distribution is central in macroeconomic analysis They focus on developing countries 5/23/2017 19 In terms of details the Structural approach focuses: Prices are set at mark-up over prime cost (the degree of monopoly – Kalecki) Saving propensities are assumed to differ by class Short-run models are set-up in variable s normalized/divided by capital stock (to emphasize growth and profit as opposed to levels of investment and payment to factors Macro balance is decomposed sectorally (stability is attained by minimizing sectoral excess demand to zero – with Jacobian checked; sector could be ‘flexi-fixi price’) 5/23/2017 20 Details of Structuralist Cont’d Imports are split in several ways (capital good a function of investment; intermediate a function of output Long-run issues are investigated by setting up transitions between steady states in which all variables growth at constant rate Ex: in one 1 sector model there are two conditions (a) the rate of money expansion and output growth should be equal, and (b) wage inflation should be equal price inflation/ real wage should be constant) Finally, direction of causality varies model to model (that is all what analysis is about) Pls read Gebre-Hiwot and Deressa who wrote along this line (Alemayehu 2004, IJEDS e-journal) 5/23/2017 21 Thank You Thank 5/23/2017 you (End of Session) 22