* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Business Cycle
Economic planning wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Italy under fascism wikipedia , lookup
Circular economy wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
Austrian business cycle theory wikipedia , lookup
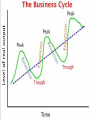
The Business Cycle The Business Cycle • Fluctuations in the market system’s economy are called business cycles. • They are measured by GDP. • As we will see more in the future, interest rates and credit expansion distort markets Phases of the Business Cycle • Expansion, or Recovery • Peak (high point) • Contraction, or Recession – 6 months or more of decline in GDP • Trough (low point) Influences on the Business Cycle • Business Investment – investment in capital goods like new machinery – promotes expansion; increases demand, efficiency, and technological change • Money and Credit – businesses borrow more money when interest rates are low and less when rates are high – total output changes as availability and affordability of credit rise and fall • Public Expectation (expectations about future economic conditions shape current economic behavior) • External Factors – changes in the world’s economic or political climate – examples: oil prices, war, etc. Predicting the Business Cycle • Businesses use predictions for plans to hire, expand, modernize, etc. • Gov’ts use predictions when developing taxation and spending policies • We use economic indicators to give us information about the business cycle Leading Indicators • indicators that usually change before the economy as a whole changes. They tell us where we are going • they are therefore useful as short-term predictors of the economy. • Stock market returns are a leading indicator: the stock market usually begins to decline before the economy as a whole declines and usually begins to improve before the general economy begins to recover from a slump. • Other leading indicators include the index of consumer expectations, building permits, and the money supply. • Complete list: – – – – – – – – – – Average weekly hours (manufacturing) Average weekly jobless claims for unemployment insurance Manufacturers' new orders for consumer goods/materials Vendor performance Manufacturers' new orders for non-defense capital goods Building permits for new private housing units. The Standard & Poor's 500 stock index Money Supply (M2) Interest rate spread (10-year Treasury vs. Federal Funds target) Index of consumer expectations Coincident Indicators • they change at approximately the same time as the whole economy, thereby providing information about the current state of the economy. • tells economists what phase we’re in – They tell us where we are at • There are many coincident economic indicators, such as Gross Domestic Product, industrial production, personal income and retail sales. • A coincident index may be used to identify, after the fact, the dates of peaks and troughs in the business cycle. Lagging Indicators • these usually change after the economy as a whole does. • indicate duration of phase of business cycle – They tell us how long we are going to be there • Typically the lag is a few quarters of a year. • The unemployment rate is a lagging indicator – employment tends to increase two or three quarters after an upturn in the general economy. • profit earned by a business is a lagging indicator as it reflects a historical performance • similarly, improved customer satisfaction is the result of initiatives taken in the past. REVIEW A. Business Cycle B. Contraction C. Peak D. Trough E. Leading Indicators F. Coincident Indicators G. Lagging Indicators H. Recession • Low point in the business cycle D. • A decline in the economy for 6 months or more H. • Indicate the duration of the phase of the business cycle G. • Fluctuations in the market economy A. • indicators that usually change before the economy as a whole changes E. • High point in the business cycle C. • they change at approximately the same time as the whole economy F. • Unemployment rate G. • Stock Market returns E. • GDP F. • Personal income F. Boom/Bust Cycle Video • \\Atlas\vol1\home\kshook\Kirk\Classes\Econo mics (9 wks.)\Unit III - Economic Indicators\Boom Bust Cycle Rap Video.flv Boom/Bust Video • Now, read through the lyrics to the song and answer the questions at the end