* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Modelling the Great Transition
Survey
Document related concepts
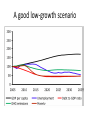
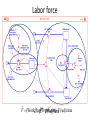
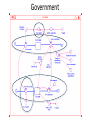
Transcript
Modelling the Great Transition Emanuele Campiglio James Meadway Istanbul – ESEE Conference - 2011 nef Great Transition Initiative • Towards a new economic system: • Widespread wellbeing • Environmental sustainability (energy, climate) • Fair distribution of wealth • But: How to get there? • We need: 1. Policy analysis tools 2. Appropriate economic theory We need a model! Starting reference • Peter Victor’s LOWGROW Model (2008) • Macroeconomic model of the Canadian Economy • System dynamics methodology • Main result: using the right policies, it could be possible to have a high employment sustainable economy without growth. • Main policies: 1. 2. Carbon taxation Work time reduction A good low-growth scenario What next? 1. Other countries’ application (UK, US, Italy, Austria, New Zealand..) 2. Economic theory refinement and expansion: – – – – – – Money Banking system Endogenous technical change Energy sector Climate change economics Rest of the world (trade, migration..) 3. Methodology refinement (system dynamics literature) The Great Transition model • Research question: How to manage the UK economy within environmental limits whilst delivering increasing wellbeing? • Research process: 1. Build a macroeconomic model of the UK economy • System dynamics methodology • Core economic model • Environmental limits; Finance; Wellbeing; Technical change; … • Data collection; functions estimation; calibration 2. Policy testing 3. Introduce microeconomic behaviour consumption / work / investment choices) (endogenous Main references • • • • • • • Peter Victor’s LOWGROW Yamaguchi’s Macroeconomic dynamics David Wheat’s Macrolab Tom Fiddaman’s FREE Millennium Institute’s T21 Neoclassical models: Dice/Rice, Witch Growth theory The core model 1 Y= min (aggr. demand, inventory) Y min (Desired full GDP) AK L capacity Y output, C Ioutput+ G Production in LowGrow Population dynamics Labor force * * Y ˆ L* ˆ F (Work.Pop* SR / w F)/adj.time L (L F part.ratioL) /adj.time Capital stock * * ˆ K (K K (1K) )YLR*/adj.time /(i ) Consumption sector * ˆ *(C C cBanking sector f (i, p,..) C cY C)d /adj.time 0 Government Next steps • Complete the core model: – Prices, interest rate, wages – Banking system, finance, money creation – Government revenues and expenditures • Insert environmental limits: – Energy sector – Climate change Energy sector sketch Next steps • Complete the core model: – Prices, interest rate, wages – Banking system, finance, money creation – Government revenues and expenditures • Insert environmental limits: – Energy sector – Climate change (damage function?) • Calibrate the model Numerical simulations: – What mix of policies is needed? – How to finance the transition? Thanks! www.neweconomics.org [email protected] [email protected]