* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GNP deflator
Survey
Document related concepts
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
Chinese economic reform wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
Gross domestic product wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
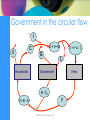
Economics TENTH EDITION by David Begg, Gianluigi Vernasca, Stanley Fischer & Rudiger Dornbusch Chapter 15 Introduction to macroeconomics ©McGraw-Hill Companies, 2010 Macroeconomics is ... • the study of the economy as a system • it deals with broad aggregates • but uses the same style of thinking about economic issues as in microeconomics. ©McGraw-Hill Companies, 2010 Some key issues in macroeconomics • Inflation – the rate of change of the general price level • Unemployment – a measure of the number of people looking for work, but who are without jobs • Output – real gross national product (GNP) measures total income of an economy – it is closely related to the economy's total output ©McGraw-Hill Companies, 2010 More key issues in macroeconomics • Economic growth – increases in real GNP, an indication of the expansion of the economy’s total output • Macroeconomic policy – a variety of policy measures used by the government to affect the overall performance of the economy ©McGraw-Hill Companies, 2010 Inflation in the UK, 1960-2010 0 5 10 % 15 20 25 UK Inflation 1960-2010 1960 Economic 1970Trends Annual 1980 Supplement, 1990 Labour 2000 2010 Source: Market Trends Year Source: ONS ©McGraw-Hill Companies, 2010 Unemployment in UK and USA Unemployment 1960-2010 UK USA 12 10 8 6 4 2 ©McGraw-Hill Companies, 2010 2009-10 1991-08 1982-90 1974-81 1960-73 0 Government in the circular flow I C S Households C+I+G G C + I + G - Te Te Government Firms B - Td Y Y + B - Td ©McGraw-Hill Companies, 2010 Adding the foreign sector • To incorporate the foreign sector into the circular flow, • we must recognise that residents of a country will buy imports from abroad, • and that domestic firms will sell (export) goods and services abroad. ©McGraw-Hill Companies, 2010 GDP and GNP • Gross domestic product (GDP) – measures the output produced by factors of production located in the domestic economy • Gross national product (GNP) – measures the total income earned by domestic citizens • GNP = GDP + net income from abroad ©McGraw-Hill Companies, 2010 Three measures of national output • Expenditure – the sum of expenditures in the economy – Y=C+I+G+X-Z • Income – the sum of incomes paid for factor services – wages, profits, etc. • Output – the sum of output (value added) produced in the economy ©McGraw-Hill Companies, 2010 National income accounting: a summary NYA G GNP (& GNI) at market prices NYA Depreciation Indirect taxes I NX NYA: Net income from abroad rental income Profits GDP at NNP Selfmarket at basic employment National prices prices income Wages and salaries C ©McGraw-Hill Companies, 2010 UK national accounts 2008 (£bn, current prices) Income measure Income measure At market prices: Income source C by households 891 Employment 770 Profits and rents Other 429 83 1282 C by government and non-profit 350 organizations I by private firms and government 245 GDP at basic prices NX –40 Indirect taxes GDP at market prices 1446 GDP at market prices Net property income from abroad GNP (GNI) at market prices 164 1446 25 1471 ©McGraw-Hill Companies, 2010 Source: www.statistics.gov.uk What GNP does & doesn’t measure • Some care is needed: – to distinguish between real and nominal measurements – to take account of population changes – to remember that GNP is not a comprehensive measure of everything that contributes to economic welfare ©McGraw-Hill Companies, 2010 GNP Deflator • The GNP deflator is the ratio of nominal GNP to real GNP, expressed as an index. Nominal GNP (Current £bn) GNP deflator (1995=100) Real GNP (£bn 1995 prices) ©McGraw-Hill Companies, 2010 1960 25 8 316 1995 750 100 750 2008 1471 141 1043 GNP per capita: Growth, 1980– 2008 (% per annum) Real GNP Denmark UK Jordan 2.3 2.7 4.1 Source: World Bank ©McGraw-Hill Companies, 2010 Per capita real GNP 2.2 2.3 0.1 Tax evasion • The hidden economy is often linked to tax evasion. • Taxes are evaded by smugglers and drug dealers but also by gardeners, plumbers and everyone else doing things ‘for cash’. • Since GNP data are based on tax statistics, the ‘hidden’ economy is unreported. This means that official GNP statistics may substantially understate the true value of GNP. • Estimating the size of the hidden economy is obviously difficult. ©McGraw-Hill Companies, 2010 Recent estimates by Schneider, Buehn and Montenegro • • • • • • • • United States UK China Germany Spain India Poland Georgia 9.0% 13.2% 14.3% 16.7% 23.1% 25.6% 29.1% 72.5% As a percentage "official" gross domestic product ©McGraw-Hill Companies, 2010