* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation by Yongguo
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Resilient control systems wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
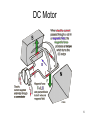
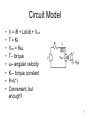
Energy Model and Measurement for DC Motors in PPRK Yongguo Mei Sep. 18, 2003 1 Outline • • • • PPPK Energy model Experiment design Future work 2 PPRK • Palm Pilot Robot Kit • Cheap, easy to build, and fun • Created by two Carnegie Mellon Robotics Institute research groups • Desktop Robotics, fully autonomous robot controlled by a Palm handheld computer • Open resource available from their website 3 PPPK (continued) • Central control Unit: BrainStem, General Purpose Module • 3 MX-400 Servo Motors, driving three wheels • 3 GP2D12 infrared sensors • Connect to PDA through RS-232 4 Power source and consumers • Source: Hobbico HydriMax 6.0V Battery, or 4 regular AA alkaline batteries, precious • Consumers: GP module, sensors, DC motors • Not consider PDA here • Concentrated on the speed control of motors to save energy 5 DC Motor 6 Circuit Model • • • • • • • • V = iR + Ldi/dt + Vemf T = Kti Vemf = Ktω T– torque ω– angular velocity Kt – torque constant P=V*i Convenient, but enough? 7 Other factors • • • • • • Saturation caused by high current Non-linear commutation effect Eddy current losses Frictions No general accepted model How do we handle all of these? 8 From another direction • Real measurement to get the energy model for our Robot? • Few people did this before • Avoid the complicated theoretical analysis • A viable way for our problem 9 Possible format • For specific Motors and working environment, Power is a function of the velocity and acceleration • What are possible formats? • Polynomials with highest exponent 2 • P(v,a) = c(1)v*v+c(2)v*a+c(3)a*a+c(4)v+c(5)a+c(6) 10 Possible format • Second-degree polynomial is enough • It can incorporate most of the factors mentioned previously • Compare this with other models • Can this model be extended to other Robots? 11 Experiment design • MX-400 Pro Servo motor • Three lines: ground, power and control • Measure voltage and current by Data Acquisition, DAQ • Program by Labview to process the data 12 Experiment Design • Accerelation, constant speed and Deceleration • Rotation • Speed control by c program, hope not too difficult! 13 Future work • • • • Real measurement Energy optimal control Motion planning Multimover problems 14