* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ELECTRIC MOTORS
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Electric bicycle wikipedia , lookup
Overhead line wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
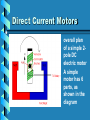
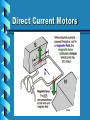
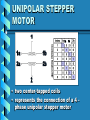
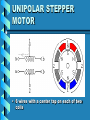
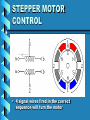
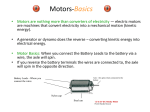
ELECTRIC MOTORS An Introduction to DC and Stepper Motors Electric Motors • Electric motors are everywhere! • In your house, almost every mechanical movement that you see around you is caused by an AC or DC electric motor. Direct Current Motors • overall plan of a simple 2pole DC electric motor • A simple motor has 6 parts, as shown in the diagram Direct Current Motors Direct Current Motors Brushed DC Motor • The brushed DC motor is one of the earliest electric motor designs • Easy to understand design • Easy to control speed DC STEPPER MOTORS • Stepping motors are electric motors without commutators • Commutation is handled externally by the motor controller • Controller charges opposite coils attracting the center rotor magnets DC STEPPER MOTORS DC STEPPER MOTORS • Voltage Rating – provides desired torque • Resistance-per-winding determines – the current draw of the motor – Maximum operating speed • Degrees per Step – Sets the number of degrees the shaft will rotate for each full step UNIPOLAR STEPPER MOTOR • Relatively easy to control • simple 1-of-'n' counter circuit can generate the proper stepping sequence • 1 transistor per winding UNIPOLAR STEPPER MOTOR • two center-tapped coils • represents the connection of a 4 phase unipolar stepper motor UNIPOLAR STEPPER MOTOR • 6 wires with a center tap on each of two coils IDENTIFYING WIRES • Check make and model to see if wire colour code is available • Observe the wires to see if you can identify groups of 3 wires • Measure resistance between wires • Wire with lowest resistance is power wire IDENTIFYING WIRES • 6 wire motors – Groups of 3 wires – 1 power & 2 signal • 5 wire motors – 1 power & 4 signal wires • power wire has lowest resistance to the others CONTROL PROGRAM • Once wires identified and connected to the circuit: a program is needed to run the motor • Example Turing Program: loop parallelput (1) delay (500) parallelput (2) delay (500) parallelput (4) delay (500) parallelput (8) delay (500) end loop STEPPER MOTOR CONTROL • 4 signal wires fired in the correct sequence will turn the motor