* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2# Power Amplifier
Standby power wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
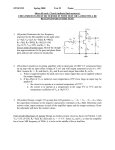
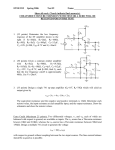
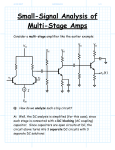
POWER AMPLIFIER Class B Class AB Class C CLASS B POWER AMPLIFIER Consists of complementary pair electronic devices One conducts for one half cycle of the input signal and the other conducts for another half of the input signal When the input is zero, both devices are off, the bias currents are zero and the output is zero. Ideal voltage gain is unity For input larger than zero, A turn ON and supplies current to the load. For input less than zero, B turn ON and sinks current from the load Complimentary Push-Pull Circuit CROSSOVER DISTORTION DEAD BAND The Ideal Class B i Cn iCn Vp RL sin t iCn vo V p sin t i Cp vo VP sin t Vp RL sin t • Maximum possible value of Vp is VCC vCEn VCC V p sin t • The instantaneous power in Qn is; pQn vCEniCn Vp pQn VCC V p sin t sin t RL The average power in Qn is PQn VCCV p RL Vp 2 4 RL Differentiating for maximum PQn with respect to Vp equal to zero gives us dPQn VCC 2V p 0 dV p RL 4 RL then VP 2VCC Maximum average power dissipation; 2 VCC PQn max 2 RL The average power delivered to the load is PL 2 RL V Power source supplies half sinewave of current, I S p RL the average value is; Vp PS Ps VCC I S VCC RL 2 V 1 p The total power supplied by the two sources is Vp PS 2VCC I S 2VCC RL The efficiency is 2 V 1 P 2 RL VP CC RL PL PS 2V maximum 4 V p 4VCC efficiency when VP VCC 0.785 78.5% Class AB Power Amplifier Small quiescent bias on each output transistor to eliminate crossover distortion Class C Power Amplifier Class AB Voltage Transfer Curve Collector Currents & Output Current iCn iL iCp Example The parameters are VDD=10V, RL=20Ω. The transistor are matched and K=0.2A/V2, VT=1V, IDQ=0.05 when vo=5V. Determine the required biasing in a MOSFET class AB output stage. Inductively Coupled Amplifier The maximum possible average signal power delivered to the load 2 PL (max) 1 1 VCC 2 I CQ RL 2 2 RL The possible average signal power supply by VCC PS VCC I CQ VCC RL 2 The maximum possible power conversion efficiency PL (max) (max) PS 2 1 VCC 2 RL VCC 2 RL 1 0.5 50% 2 TRANSFORMER COUPLED AMPLIFIER






















![Tips on Choosing Components []](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007788582_1-9af4a10baac151a9308db46174e6541f-150x150.png)