* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Van der Pol
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Chirp spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
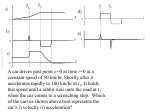
Van der Pol Convergence The damped driven oscillator has both transient and steady-state behavior. q • Transient dies out • Converges to steady state q 2q 02 q f cos t 2 f cos t arctan 2 2 0 q ae t cos 02 2 t 02 2 2 4 2 2 q Equivalent Circuit L vin C • Inductance as mass • Resistance as damping • Capacitance as inverse spring constant v R q C dq vR Ri R dt vout vC vL L Oscillators can be simulated by RLC circuits. d 2 v R dv 1 2 v V0 sin t 2 dt L dt LC 2 di d q L 2 dt dt vin vL vC vR 0 R 2L 02 1 LC Negative Resistance Devices can exhibit negative resistance. • • Negative slope current vs. voltage Examples: tunnel diode, vacuum tube These were described by Van der Pol. R. V. Jones, Harvard University d 2v d 3 2 2 v v v V0 sin t 0 2 dt dt Steady State v 12 V (t )e it c.c. • Time varying amplitude V • Slow time variation 1 2 0 2 V iV 2 2V0 1 3 2 i V V i 0 2 4 2 V 2 4 3 Assume an oscillating solution. The equation for V follows from substitution and approximation. The steady state is based on the relative damping terms. Frequency Locking V (t ) V ei(t ) V 1 3 2 V V V 0 cos 2 4 2 2 2 V0 sin 0 2 2V d l sin l V0 2V 3V0 8 The amplitude term can be separated. • Two coupled equations • Detuning term d • Locking coefficient l The detuning is roughly the frequency difference. For small driving force the locking coefficient depends on the relative damping. Relaxation Oscillator The Van der Pol oscillator shows slow charge build up followed by a sudden discharge. The oscillations are self sustaining, even without a driving force. y 1 y 2 y y 0 Wolfram Mathworld Limit Cycle The phase portraits show convergence to a steady state. This is called a limit cycle. next