* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download current & charge
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
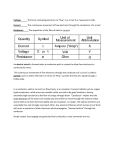
What we will do today • State what is meant by electric current. • State the difference between conductors and insulators. • State how we measure electric current. • State how we can measure electric charge. What is Electric Current? • In a conductor, electrons are allowed to move freely. • An electric current is a flow of electric charges, usually electrons. • Electrons are very small negatively charged particles. • In a closed circuit electric current moves from the negative terminal to the positive terminal of a battery or power source. Conductors and Insulators • Conductors – allow electric current to flow through. • E.g metals and carbon • Insulators – do not allow electric current to flow through. • E.g. non-metals like air, plastic & wood • Super Electric Human (India) Who can Conduct High Voltage Electricity Through his Body.FLV - YouTube Measuring Electric Current • An ammeter is an instrument that measures electric current. • Electric current has the unit amperes (A). Measuring Electric Charge • Electric ‘current’ is a flow of electric ‘charge’ around a circuit. • We find that the relationship between the two is given as: Charge = Current x time Q=It • Charge is measured in Coulombs (C). Example 1 • I=5A • t = 30 s • Q=? Example 2 • I=? • t = 5 mins • Q = 150 C Example 3 • I = 100 mA • t=? • Q=5C 2005, Qu: 9