* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download powerpoint file
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Standing wave ratio wikipedia , lookup
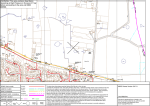
Electrical Contractor Unit solution Cable selection commentary Quantity Load Load Group Diversity 12 60W lights A 3A 1-20 points + 2A Next 20 or part there of 8 L.V down lights 0.4A each A 1 100W Sensor Light A 6 Double 10A 230V outlets B(i) 12 points 2 Single 10A 230V outlets B(i) 2 points 1 300W Tastic B(i) 1 point = 15 points total 1 5KW Wall oven C 1 6KW Hot plate C 50% full load (11000/230)X 0.5 1 3KW continuous HW unit F Full load 3000/230 1 3.5KW Fixed Space Heater D 3500/230 x 0.75 M.D. Units 1to5 5 10A 23.92 13 M.D. 11.42 63.33A Quantity Load Load Group Diversity 12 60W lights A 3A 1-20 points + 2A Next 20 or part there of 8 L.V down lights 0.4A each A 1 100W Sensor Light A 6 Double 10A 230V outlets B(i) 12 points 2 Single 10A 230V outlets B(i) 2 points 1 300W Tastic B(i) 1 point = 15 points total 1 5KW Wall oven C 1 6KW Hot plate C 50% full load (11000/230)X 0.5 1 3KW continuous HW unit F Full load 3000/230 1 Heat pump 8.7 A each D No contribution less than 10A Consider as an additional outlet M.D. Units 6 to 9 5 10A 23.92 13 M.D. 51.92A Quantity load Load Group Diversity C W B Communal load 1,4,7 house 2,5,8 3,6,9 2 2x36W 0.43A each H Full load 2x.43 0.86 3 1000W metal halide flood lights (6.8A) each H 3x6.8 = 20.4 2 10A 230V outlets I 2A per point 4.0 Maximum Demand Communal load 25.26 Quantity Load Group Diversity R W B 1,4,7 2,5,8 3,6,9 house 6A 6 6 6 10A + 5A x 3 =25A 25 25 25 15A 15 15 15 18 12 60W lights A 8 L.V down lights 0.4A each A 1 100W Sensor Light A 6 Double 10A 230V outlets B(i) 2 Single 10A 230V outlets B(i) 1 300W Tastic B(i) 1 5KW Wall oven C 1 6KW Hot plate C 1 3KW continuous HW unit F 6A per unit 6A x 3 = 18 A 18 18 1 3.5KW Fixed Space Heater D (7000/230) x 0.75 (3500/230 +)x0.75 22.82 22.82 Communal load 11.41 25.26 Consumers mains cable size The mains cable is X90 SDI installed in one conduit U/G. Referring to Table 3.4 item 2 Table 8 column 24, a 50mm² Cable is rated at 163A Referring to Table 41, the Vc value for a 50mm² conductor is 0.878mV/Am The Actual voltage drop in the mains is: Vc L I 0.878 10 131 Vd 1.1 5Volts 1000 1000 This Value is a three phase value and must be converted to a single phase value to determine the voltage drop allowed in the sub-mains to each unit. voltage drop single phase 1.15 1.2731 0..6647 volts 1.73 3 M S B U1 U2 10M Car Wash bay U3 20M U4 25m 35M Conduits in groups of 2 Driveway Supply Mains Conduits in groups of 2 20M 30M U6 500KVA Transformer U7 40m U8 40M U9 U5 35M Sub-main to unit 1 Referring to Table 3.4 ASNZS3008 item 1, Table 8column 24, 16mm² X90 conductor = 86A. The conduits are installed in a trench in groups of 2 separated 300mm.apart. Table 26.2 . Derating factor 0.93 (86 x 0.93 =79.98A) Table 41, the Vc value for a 16mm² conductor is 2.55mV/Am. At 90ºC Therefore: A 16mm² Conductor will satisfy current requirements Voltage drop allowed in the sub-mains is 2.3% = 5.29Volt single phase. Vd Vc L I 2.55 1.155 10 73 2.15V 1000 1000 The voltage drop in the neutral conductor is therefore 50% of this value 2.15 x 0.5 = 1.075V Sub-main to unit 9 1000Vd 1000 5.29 2.204m.V/A .m L I 40 60 This Vc value is a single phase value. To look up the cable for the sub - main this value must be converted to a three phase value first. 2.204 0.866 1.908mV/Am Vc Referring to Table 41 (ASNZS3008.1.1) a 25mm² cable has a Vc value of 1.62mV/Am at 90ºC Referring to Table 8 column 24, A 25mm² conductor can carry 113A. The de-rating factor for the arrangement are 0.8 and 0.93 131 x 0.8 x 0.93 = 84 A. Current is not the determining factor. The conductor size will need to be determined from voltage drop requirements. Therefore a 25 mm² cable is required for the sub-main to unit 9 Fault level at the transformer terminals 500KVA transformer. Assume a 5% impedance value. This value refers to the value of the primary voltage required to cause full load current with a short circuit on the secondary. With 100% primary voltage applied the short circuit current would be 20 times the full load current. 3 VL IL 1000 KVA 500 ,000 IL 722.5 A 3 400 1.73 400 100 100 Iscc Iflc 722.5 14450 A 5 5 KVA 500KVA transformer 14450A Fault Impedance at transformer Terminals V I short circuit current 230 Z(transfor mer) 14450 Z (transformer ) 0.0159ohms MSB Z(transfor mer) Sub-board Unit 1 Fault level at the point of supply 500mm² Supply Authority conductors run from the transformer. Length to the consumers mains point of supply is 29M. a.c. Resistance Table 35 = 0.0525 ohms/1000m. At 75ºC 0ne conductor. Active + Neutral = 0.0525 x 2 = 0.105 ohms/ 1000m 500KVA transformer Reactance Table 30 = 0.0700 X 2 = 0.14 ohms/1000m. Z R 2 X2 Z 0.1052 0.14 2 Z 0.175 ohms/1000m 0.175 29 mains 0.005075ohms 1000 1 Supply Mains Consumers Mains Fault level at the point of supply I 230 Z TX Z Distributors 230 I 0.0159 0.005075 I 10965A POS 10965A MSB Sub- mains Sub-board Unit 1 Fault level at the Main switch board 50mm² SDI conductor a.c. resistance is 0.426 ohms per 1000m at 45°C Table 34 Active + Neutral = 0. 426 x 2 = 0. 852 0hms/1000m Consumers mains are 10m so the phase to N resistance is 500KVA transformer 0.852 10 0.00852 ohms 1000 To determine the fault level at the main switchboard Fault level MSB 230 Ztx Z dis Zcm 230 0.0159 0.005075 0.00852 7797A MSB Sub-board Unit 1 7797A Fault level at the Unit 1 switch board 16mm² two core conductor. The a.c. Resistance is 1.26 ohms Per 1000m table 34 Sub- mains are 20m so the phase to N resistance is 1.26 10 0.0126 ohms one conductor 1000 active Neutral 0.0.0126 2 0.0252ohms 500KVA transformer To determine the fault level at the unit switchboard Fault level unit 1 DB 230 Ztx Zsc Zcm Zsm 230 0.0159 0.005075 0.00852 0.0252 4205A MSB Sub-board Unit 1 4205A Actual progressive volt drop • Although this project specified an allowable voltage drop as follows: • Consumer mains 0.5% • Sub-mains 2.3% • Final sub-circuits 2.2% • The actual voltage drop in the mains and sub-mains is less than the allowed percent. • There fore the voltage drop in the final sub-circuit can be increased Progressive volt drop POS Mains Transformer The volt drop in the mains is Vc L I Vd 1000 .878 10 145 Vd 1000 Vd 1.2731 Volts three phase 1.2731 0.73589Volts single phase 1.73 Sub-mains MSB Unit 2 SB Volt drop in the sub-main unit1 Vc L I 1000 2.43 1.155 24 63.33 Vd 1000 Vd 4.26 Volts Vd The voltage drop allowed in final sub-circuits is 11.5 – (0.73589+4.26) 6.5 Volts Maximum length of 16mm² conductor for sub-mains Units1 to 5 • The next step is to determine the maximum length a 16mm² conductor can be run allowing for a voltage drop in the final subcircuits of 2.2% 1000 Vd 1000 5.71 L max 32.13M Vc I 2.43 1.155 63.33 Units 1, 2, and 3 can be supplied with a 16mm² sub-main Units 4 and 5 require a 25mm² sub-main. Maximum length of 16mm² conductor for sub-mains units 6 to 9 • The next step is to determine the maximum length a 25mm² conductor can be run allowing for a voltage drop in the final subcircuits of 2.2% Vd 1000 5.711000 L max 34.8M Vc I 2.43 1.155 58.45 Units 6 and 7 can be supplied with 16mm² sub-mains Units 8 and 9 require 25mm² sub-mains Progressive volt drop POS Mains Transformer The volt drop in the mains is Vc L I Vd 1000 .878 10 145 Vd 1000 Vd 1.2731 Volts three phase 1.2731 0.73589Volts single phase 1.73 Sub-mains MSB Unit 9 SB Volt drop in the sub-main unit1 Vc L I 1000 1.55 1.155 40 58.45 Vd 1000 Vd 4.185Volts Vd The voltage drop allowed in final sub-circuits is 11.5 – (0.73589+4.185) 6.58 Volts Fault level • The fault level can be determined at each point in the installation as follows Cable Impedance ohms A + N V/Z Fault level Transformer 0.0159 230/0.0159 14450A Supply Mains 0.005075 230/(0.159 + 0.005075) 10965A Consumer Mains 0.00852 230/ (0.0159 + 0.005075 +0.00852) 7797A Sub-mains 0.0252 230/(0.0159 + 0.005075 +0.00852 +0.0252) 4205A Earth fault loop impedance. • The earth fault loop impedance can be determined as shown in the next slide. Supply Mains Active + Neutral 500mm² conductor 29m Z = 0.003659 Supply Transformer Supply Earth electrode Main switchboard Mains conductor 50mm² 10m. Zcm Active + Neutral = 0.00852Ω Sub-main Circuit breaker Main earth Electrode Sub-main Earth 6mm² Z = 0.15Ω From table 34 Unit 9 SB Sub-mains Active 40m 25mm² Zsm = 0.03536Ω Table 34 Final sub-circuit 16A Circuit breaker Final Sub-circuit Protective earth 2.5mm² Z = 0.18Ω Final sub-circuit Active 2.5mm² Route length 20m Z = 0.18Ω From Table 35 Sum of impedance values in the Earth fault-loop Device/ cable9 Impedance Ω Transformer 0.0159 Supply Mains A+N 0.003659 Consumer Mains A+N 0.00852 Sub-main Active 0.03536 Final sub-circuit active 0.18 Protective earth 0.18 Sub-main earth 0.15 Total Impedance 0.573439 Fault current in the Final sub-circuit • Table 8.1 requires a maximum value of earth fault loop impedance of 1.91Ω. The actual value for this circuit (0.573439 ohms) is below the required maximum value. • The current flowing in this fault loop will be sufficient to operate the protective device as required. 230 230 Iscc 401A Ztotal 0.573439 • This value exceeds the required value 7.5 x 16= 120A for a type C MCB