* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Power Grid in High School Physics
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Transmission line loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Grid energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
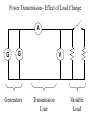
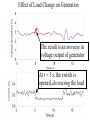
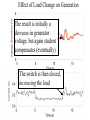
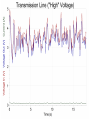
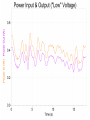
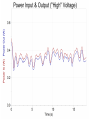
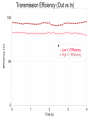
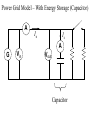
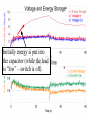
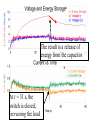
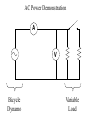
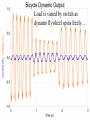
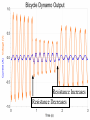
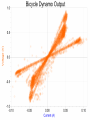
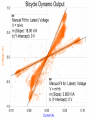
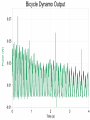
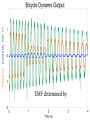
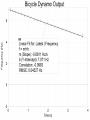
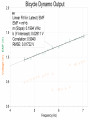
Power Grid in High School Physics (and Vice Versa!) Matthew W. Milligan Farragut High School CURENT – Research Experience for Teachers (RET) July 17, 2012 Knoxville, Tennessee Power Grid & High School Physics I. II. Frequency Disturbance - FNET data & animation - wave phenomena Modeling the Grid in the Classroom - series and parallel circuits - significance of I2R - conservation of energy - generators basics A hand-crank DC generator is used as a power source for a classroom electrical “grid” that models properties of the actual AC power grid. Students get a true hands-on experience! Data acquisition system measures voltages and currents Switches are used to simulate generator and load changes A “lamp cord” serves as the “transmission line” Students can judge the power produced by tactile feedback of their own exertion and the power consumed by visual feedback of brightness of the lamps. Experiment 1: Explore the effects of changes in generation and changes in load. Power Transmission– Effect of Load Change A G G Generators V Transmission Line Variable Load Effect of Load Change on Generation The result is an increase in voltage output of generator At t = 5 s, the switch is opened, decreasing the load Effect of Load Change on Generation Student compensates to bring the voltage back down. The result is an increase in voltage output of generator Lower current means less power needs to be generated, so less effort is needed to turn the crank Effect of Load Change on Generation The result is initially a decrease in generator voltage, but again student compensates (eventually) The switch is then closed, increasing the load Questions for Students • If the load changes, why must student(s) exert a different amount of force to crank the generator(s)? • How is there an increase in electric power delivered across the transmission line even though the voltage is not increased? • What happens in an actual power plant if there is a sudden and significant change in the load? • What differences would occur if generators are present at both ends of the transmission line? Experiment 2: Explore the effects of different transmission line voltages. Power Transmission Model – “Low Voltage” A G G Generators Vin Vout Transmission Line Load Power Transmission Model – “High Voltage” A G Vin Vout G Generators Transmission Line Load Questions for Students • Although there is clearly better efficiency delivering electric power at high voltage, what are disadvantages of the series connections? • How are the actual generators of the nation’s power grid interconnected? • How is high voltage transmission achieved? • If energy is conserved, what becomes of the wasted electrical power (accounting for difference between input and output)? Experiment 3: Explore the use of energy storage in a power grid. Power Grid Model – With Energy Storage (Capacitor) A Io Is A G Vin Vout Capacitor Initially energy is put into the capacitor (while the load is “low” – switch is off). The result is a release of energy from the capacitor At t = 31 s, the switch is closed, increasing the load AC Power? • It may be very difficult to synchronize multiple generators – but might be fun to try! • Commercially made hand-crank generators AC generators are hard to find (nonexistent?). • Bicycle “dynamos” may be adaptable for the classroom… Bicycle “dynamo” AC generator Improvised handle and flywheel Experiment 4: Vary the load on an AC generator The light can be seen to flicker as the wheel turns… AC Power Demonstration A V Bicycle Dynamo Variable Load Load is varied by switch as dynamo flywheel spins freely… Resistance Increases Resistance Decreases This represents electrical energy “extracted” from the free spinning dynamo EMF determined by AC Power – Ideas to Explore • Experiment with variations in flywheel/handle design. • Try turning the dynamo by using a falling mass hanging from string wrapped around wheel and axle. This would provide constant torque and it would be easy to determine the energy or power input.