* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Clipper
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
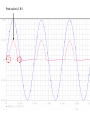
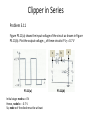
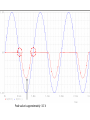
Recall Lecture 6 • Rectification – transforming AC signal into a signal with one polarity – Half wave rectifier • Full Wave Rectifier – Center tapped – Bridge • Rectifier parameters – Duty Cycles – Peak Inverse Voltage (PIV) Clipper Circuits Standard Clipper Circuits ● Clipper circuits, also called limiter circuits, are used to eliminate portion of a signal that are above or below a specified level – clip value. ● The purpose of the diode is that when it is turn on, it provides the clip value i. Find the clip value = V’. To find V’, use KVL at L1 assuming the diode is on ii. The equation is : V’ – VB - V = 0 V’ = VB + V VI V’ = VB + V L1 iii. Then, set the conditions If v > V’, what happens? diode conducts, clips and hence o = V’ If v < V’, what happens? diode off, open circuit, no current flow, o = I I v v v I EXAMPLE For the circuit shown below sketch the waveform of the output voltage, vo. The input voltage is a sine wave where vI = 5 sin t. VB is given as 1.3 V. Assume V = 0.6 V 1.3 V Solution i. Find the clip value = V’. To find V’, use KVL at L1 assuming the diode is on ii. The equation is : V’ – 1.3 - 0.6= 0 V’ = 1.9 V 1.3 V iii. Then, set the conditions If If v > V’, what happens? I v < V’, what happens? v I diode conducts, clips and hence v o = V’ = 1.9 V diode off, open circuit, no current flow, I V’ = 1.9V v =v o I EXAMPLE For the circuit shown below sketch the waveform of the output voltage, vou. The input voltage is a sine wave where vI = 10 sin t. Assume V = 0.7 V + + vI vo - - Solution i. Find the clip value = V’. To find V’, use KVL at L1 assuming the diode is on ii. The equation is : V’ – 4 + 0.7= 0 V’ = 3.3 V iii. Then, set the conditions If v > V’, what happens? diode off, open circuit, no current flow, v = v If v < V’, what happens? diode conducts, clips and hence v o I o= I VI L1 V’ = 3.3V I V’ = 3.3 V Parallel Based Clippers Positive and negative clipping can be performed simultaneously by using a double limiter or a parallel-based clipper. The parallel-based clipper is designed with two diodes and two voltage sources oriented in opposite directions. This circuit is to allow clipping to occur during both cycles; negative and positive Clipper in Series ECE 1201 The input signal is an 8 V p-p square wave. Assume, V = 0.7 V. Sketch the output waveform, vo. c b a vo Initial stage: node a = 0V Hence, node b = 1.5 V So, node c of the diode must be at least 2.2 V • Hence, the positive cycle of the square wave has met the condition of 2.2 V • Perform KVL as usual: – 4 + 0.7 + 1.5 + vo = 0 vo = 1.8 V 4 1.8 -4 • What if now the input is change to 4 sin t? • It has to wait for the input signal to reach 2.2 V. Before that, the output, vo is zero as diode is off. • Perform KVL as usual: – 4 + 0.7 + 1.5 + vo = 0 vo = 1.8 sin t V Peak value is 1.8 V • So, basically, clipper in series clips at zero. It is similar to half wave where the diode only turns on during one of the cycle. Clipper in Series Problem 3.11 Figure P3.11(a) shows the input voltage of the circuit as shown in Figure P3.11(b). Plot the output voltage vo of these circuits if V = 0.7 V c P3.11(a) Initial stage: node a = 0V Hence, node b = - 0.7 V So, node c of the diode must be at least -1.9 V b P3.11(b) a • Hence, the negative cycle of the square wave has met the condition of |1.9| V • Perform KVL as usual: + 3 - 0.7 - 1.2 + vo = 0 vo = - 1.1 V vo - 3V + -1.1 -1.1 • What if now the input is change to 5 sin t ? • It has to wait for the input signal (negative cycle) to reach |1.9| V. Before that, the output, vo is zero as diode is off. • Perform KVL as usual: + 5 - 0.7 - 1.2 + vo = 0 vo = -3.1 sin t V Peak value is approximately -3.1 V