* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
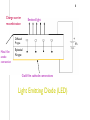
1 DATE : 03/10/2012 BRANCH : ECE (3rd SEM.) ROLL NO : E11029 HELLO EVERYONE, MYSELF MOHAN SHYAM I AM REPRESENTING THE TOPIC”LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (LED)” SUB : ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS (EDC) An LED is a specially fabricated P-N junction diode that emits monochromatic light when it is forward biased. LED is invented 1st by “OLEG LOSEV “in 1927. First practical of visible spectrum (red) was developed in 1962 by “NICK HOLONYAK ”. so He is called the FATHER of LED. In 1968 “Man Santo company” was the first organization to mass produce visible LEDs using GaAsp . The lifetime of LEDs are 25000 to 100000 hours. But heat and current setting can extend or shorten this time. 2 3 The operation of LED is based upon the phenomenon of electroluminance When a P-n junction is f/w biased then free electrons cross the N-region and recombine with holes existing in p-region . free electrons are in C.b. (high energy level) while holes are in V.b. ( low energy level). As these electrons fall from higher energy to lower energy level recombine with holes then these radiated energy in the form of heat and light Led produces light while conducting current through them so led are current driven devices. 4 Diagram of LED Working of LED 5 The color of light emitting diode depends upon various factors such as 1 used semiconductor material 2 energy band gap 1 Using various semiconductors material If the used material is GaAsP (Gallium arsenide phosphide) then LED emit either red or yellow light. If the used material is GaAs (gallium arsenide) then LED emit invisible infrared light. If the used material is GaP then LED emit either red or green light. 2 By energy band gap if the energy band gap of the electron (low energy electron cross the barrier) is small then the LED emit infrared or red light . If the energy band gap is large (highly energetic electrons cross the barrier) then the LED emit blue or violet color. 6 Charge carrier recombination Metal film anode connection Emitted light Diffused P type + Epitaxial N type - Gold film cathode connections Light Emitting Diode (LED) Vs 7 1 They work on low voltage(1-2v) and low current (10-30ma) and consume low power(10-100mv). 2 They require no warm-up time they have fast on-off switching(less than 1ns). 3 They are small in size and light in weight so they occupy small space. 4 They can emit different colored lights. 5 They can emit invisible radiation. 6 LEDs can be operated over a wide temperature ranges (0-70c). 8 Cathode +Vs I = (VS-Vd)/Rs Rs I Vd Anode Symbol of LED LED circuit LED BRIGHTNESS 9 The brightness of light emitted by an LED depends upon the current flowing through it. When Vs is greater than Vd then the brightness of the led is approximately constant. The best way to control the brightness is to derive the LED with a constant current source. And thus the brightness of the LED remains constant because the current is constant. APPLICATION OF LED 1 LEDS are used in the seven segment display devices 2 These are used in voltage polarity tester 3 These are used as continuity tester Thank You