* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Electrical connector wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
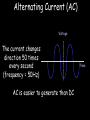
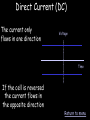
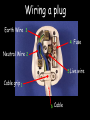
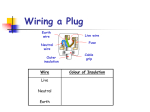
Electricity Menu • AC & DC • Household Plugs & Fuses • Power & Fuses AC & DC Alternating Current (AC) Voltage The current changes direction 50 times every second (frequency = 50Hz) AC is easier to generate than DC Time Direct Current (DC) The current only flows in one direction Voltage Time If the cell is reversed the current flows in the opposite direction Return to menu Household Plugs & Fuses Wiring a plug Earth Wire 3 4 Fuse Neutral Wire 2 5 Live wire Cable grip 1 6 Cable Errors in Wiring Plugs 1. Bare wires showing 2. Proper fuse not installed 3. Earth Wire not connected 4. Live & Neutral wrong way round 5. Cable Grip loose Dangerous Practices With Mains Electricity 1. Broken Plugs & Frayed Cables 2. Plugs & Cables near water 3. Overloaded sockets 4. Wet hands whilst using electricity The Earth Wire Earth wires are always used in appliances with a metal case. If a fault develops in the appliance causing the live wire to touch the case, there is a surge in the current down the earth wire. This causes the fuse to blow. Live & Neutral The Live wire alternates between high positive and high negative voltage with an average of about 230V The neutral wire is always at 0V. Electricity normally flows in and out of the live and neutral wires only Fuses Symbol Car fuses A Fuse is a deliberate weak spot in a circuit How Does a Fuse Work? Fuses are designed for safety. If a fault develops causing the live and neutral (or earth) wire to cross, a large current flows through the fuse and causes it to melt. This breaks the circuit and protects the appliance and user. Complete the descriptions….. Fuse A deliberate weak spot. Melts and breaks the circuit with too much current Earth Wire Neutral Wire Live Wire Cable Grip Casing Brass Pins Return to Menu Power & Fuses Power, Current & Voltage Power is “the rate of doing work”. The amount of power being used in an electrical circuit is given by: Power = voltage x current (W) (V) P (A) The unit of power is the watt (W) V X I Power and Fuses Complete the following table: Appliance Power Rating Voltage (V) (W) Toaster 950 230 Electric Fan Heater 2200 230 Hairdryer 330 230 Floor Cleaner 1050 230 Computer 200 230 HiFi 80 230 Current (A) Fuse Required (3, 5 or 13A) Return to Menu