* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evaluation of Subthreshold Design Techniques
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
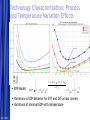
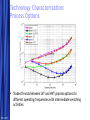
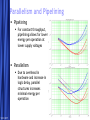
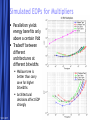
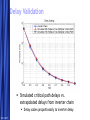
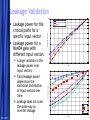
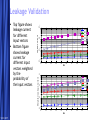
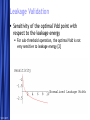
Circuit Design Techniques for Low Power DSPs Simone Gambini Marghoob Mohiyuddin Melinda Ler Motivation Energy Per Operation (EOP) important For energy-constrained systems, e.g., battery-powered devices Supply voltage scaling can be used to reduce energy consumption Leakage limits scaling to above a certain supply voltage Conventional techniques for low power/energy design may not be beneficial Low power designs also have performance constraints (apart from power) Design should meet throughput constraints while minimizing energy consumption Want to explore tradeoffs in design given these constraints 5/23/2017 Free Template from www.brainybetty.com 2 Problem Statement Study the impact of low power design techniques for different circuits with performance constraints Effects of process variations and temperature Supply voltage scaling Using parallelism to reduce power Architectural approaches Multiplier designs used as case studies Fundamental block in many DSP systems 5/23/2017 Free Template from www.brainybetty.com 3 Prior Work If energy per operation (EOP) used as an optimization metric then an optimal choice of Vdd exists [1] Technology, micro-architecture and architecture affect the EOP Minimum EOP point at EOP optimal Vdd shown to shift with different microarchitectures [2] Performance constraint not taken into account 5/23/2017 Free Template from www.brainybetty.com 4 Project Outline Technology characterization Simulated leakage and delay for 90nm technology node across process corners and temperature Modeling EOP Using simulated delay and leakage data for FO1 and FO4 ring oscillators Extrapolated to get predictions for EOP behavior for different micro-architectures Characterizing test circuits to validate our predictions Delay validation Power validation 5/23/2017 Free Template from www.brainybetty.com 5 Technology Characterization: Process and Temperature Variation Effects EOP Model EOP V dd 1 V th n U T 2 C K L e C tot V dd L fit d Variations in EOP behavior for SVT and LVT across corners Variations of minimal EOP with temperature 5/23/2017 Free Template from www.brainybetty.com 6 Technology Characterization: Process Options Tradeoff exists between LVT and HVT process options for different operating frequencies with intermediate switching activities 5/23/2017 Free Template from www.brainybetty.com 7 Parallelism and Pipelining Pipelining For constant throughput, pipelining allows for lower energy per operation at lower supply voltages Parallelism Due to overhead in hardware and increase in logic delay, parallel structures increases minimal energy per operation 5/23/2017 Free Template from www.brainybetty.com 8 Case Study: Multipliers Investigated multiple architectures Wallace tree multiplier Array multiplier Serial multiplier Impact of parallelism on EOP behavior Technology characterization predicts that parallelism increases EOP for low supply voltages • Leakage becomes the dominating factor at low supply Higher leakage factor means optimal Vdd should increase with parallelism 5/23/2017 Free Template from www.brainybetty.com 9 Flow for EOP estimation Circuit synthesis (Module Compiler) Extraction of activity factor (ModelSim) Correlated input vectors generated with Matlab Gates annotated with activity factors and capacitances Delay simulation for critical paths (Spectre) Over multiple Vdds Power estimation (PowerPrime) Dynamic and leakage power for single supply voltage Power scaling with Vdd extrapolated using scaling factors from FO4 inverter chain 5/23/2017 Free Template from www.brainybetty.com 10 Simulated EOPs for Multipliers Parallelism yields energy benefits only above a certain Vdd Tradeoff between different architectures at different bitwidths Wallace tree is better than carry save for higher bitwidths Architectural decisions affect EOP strongly 5/23/2017 Free Template from www.brainybetty.com 11 Delay Validation Simulated critical path delays vs. extrapolated delays from inverter chain Delay scales proportionally to inverter delay 5/23/2017 Free Template from www.brainybetty.com 12 Leakage Validation 10 A large variation in the leakage power over input vectors Total leakage power depends on the statistical distribution of input vectors over time Leakage does not scale the same way as inverter leakage 5/23/2017 Normalized Leakage 16b Adder Critical Path 64b Adder Critical Path Inverter 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 Vdd Normalized Leakage for Different Input Vectors 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 Normalized Leakage Leakage power for the critical paths for a specific input vector Leakage power for a NAND4 gate with different input vectors 0 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0000 0001 0011 0111 1111 Inverter 0.2 0.1 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 Free Template from www.brainybetty.com 0.4 0.5 0.6 Vdd 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 13 Leakage Validation Leakage Current 10 10 10 10 -7 0000 0001 0011 0111 1111 -8 -9 -10 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 Vdd -7 10 Weighted Leakage Current Top figure shows leakage current for different input vectors Bottom figure shows leakage current for different input vectors weighted by the probability of the input vectors 1111 0111 0011 0001 0000 -8 10 -9 10 -10 10 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1 Vdd 5/23/2017 Free Template from www.brainybetty.com 14 Leakage Validation Sensitivity of the optimal Vdd point with respect to the leakage energy For sub-threshold operation, the optimal Vdd is not very sensitive to leakage energy [2] 5/23/2017 Free Template from www.brainybetty.com 15 Conclusions & Future Work For low power systems operating below a certain operating frequency, parallelism would not be the ideal option due to leakage This trend is expected to be reinforced in the future technology nodes Fast and accurate leakage estimation tools needed Should take into account the state-dependent behavior of leakage 5/23/2017 Free Template from www.brainybetty.com 16 References [1] D. Markovic, V. Stojanovic, B. Nikolic, M. A. Horowitz, and R. W. Brodersen, “Methods for True Energy-Performance Optimization,” IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, vol. 39, pp. 1282–1293, Aug. 2004 [2] B. H. Calhoun and A. Chandrakasan, “Characterization and Modeling of Minimum Energy Per Operation Point,” in Proc. IEEE International Symposium on Low Power Electronics and Design, Newport Beach, California, Aug. 2004, pp. 90–95. [3] A. Wang and A. Chandrakasan, “A 180mV FFT Processor Using Subthreshold Circuit Techniques,” in Proc. IEEE International SolidState Circuits Conference, Feb. 2004. [4] Y. Taur and T. H. Ning, Fundamentals of Modern VLSI Devices. Cambridge University Press, 1999. 5/23/2017 Free Template from www.brainybetty.com 17