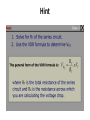
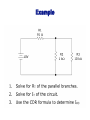
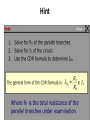
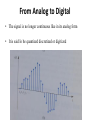
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 1 - Rabie Ramadan
Phase-locked loop wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Direction finding wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope wikipedia , lookup
Broadcast television systems wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Radio direction finder wikipedia , lookup
Signal Corps (United States Army) wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Beams wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular repeater wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunication wikipedia , lookup
Analog television wikipedia , lookup