* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Loading coil wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Standby power wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Distributed control system wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power supply wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
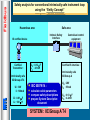
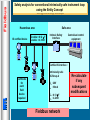
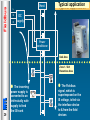
FISCO 1 Fieldbus Fieldbus Safety analysis for conventional intrinsically safe instrument loop using the “Entity Concept” Hazardous area Intrinsic Safety Interface IS certified device Certified Transmitter : Safe area Cc : 0.12 m F Lc : 4.1mH Intrinsically safe IIC/Group A T4 Ui : 30V Ii : 100mA Ci : 0.01 m F Li : 100 m H IEC 60079/14 : calculate cable parameters compare safety descriptions prepare System Descriptive document Centralised control equipment Certified IS interface : Intrinsically safe IIC/Group A Uo : 28V Io : 93mA Co : 0.13 m F Lo : 4.2mH SYSTEM : IIC/Group A T4 Fieldbus Safety analysis for conventional intrinsically safe instrument loop using the Entity Concept Hazardous area IS certified device Safe area C:cable = 0.12 m F L:cable = 4.1mH Intrinsic Safety Interface Centralised control equipment Certified IS interface : Intrinsically safe IIC/Group A Certificate for each field device required Uo : 28V Io : 93mA Co : 0.13 m F Lo : 4.2mH Fieldbus network Re-calculate if any subsequent modifications Fieldbus FF-816 Physical Layer Profile Specification for hazardous area devices recommends minimum input voltage current & power levels maximum input capacitance & input inductance FF-816 Ci 4 Ui 24 Volts Ii 250 mA Pi 1.2 watts Ci 5 nF Li 20 uH Bus interface output parameters Field device input parameters Fieldbus Fieldbus Intrinsically Safe Concept (FISCO) PTB, the German Test Authority, in collaboration with German industry, examined the intrinsically safe needs of the 31.25 kbit/s physical layer of Fieldbus and developed an approach which is applicable to IEC 61158-2 the physical layer employed by both Profibus ‘PA’ & Foundation Fieldbus ‘H1’ systems A PTB report dated August 1994 provided details of the experimental evidence, from which the IEC standard has emerged The resulting document covers all aspects of a low frequency Fieldbus system allows a system to be built with only a minimum analysis of the safety requirements allows very simple documentation 5 Fieldbus The FISCO model published in 1994 IEC 60079-27 defines the FISCO model “Fieldbus Intrinsically Safe Concept” provides clear guidelines for the design & installation of fieldbus networks in explosion protected environments Fieldbus network Foundation Fieldbus H1 & Profibus PA Host interface Tree Spur Daisy-chain 6 Fieldbus Fieldbus Intrinsically Safe Concept (FISCO) The experimental work covered a defined range of cable parameters, circuit voltage & current; hence the permitted cable parameters in a FISCO IS circuit are limited to : Parameter Loop resistance Loop inductance Capacitance Max length of each spur cable Max length of each trunk cable 15 ohm 0.4 mH 80 nF Value to 150 ohm / km to 1 mH / km to 200 nF / km 30 m in IIC & IIB 1 km in IIC & 5 km in IIB Table 1 - FISCO cable parameters 7 These limits are not difficult to achieve, since a typical Fieldbus trunk cable has parameters of : 50 /km, 0,8 mH/km & 120 nF/km The length of the trunk is usually determined by the operational requirements. Fieldbus Fieldbus Intrinsically Safe Concept (FISCO) The original Foundation Fieldbus specification (FF-816; IEC61158-2) was for a ‘ia IIC’ resistive power supply, which suffers from very restrictive voltage & current 18.4V V Resistive I MTL5053 non-FISCO EEx II (1) GD EEx [ia] IIC [-20 OC to +60 OC] 8 80 mA Fieldbus Fieldbus Intrinsically Safe Concept (FISCO) The FISCO standard examined the ignition capability of constant current power supplies it proposed acceptable levels of power for supplies with a ‘trapezoidal’ characteristic, as opposed to those with a falling, resistor-limited characteristic. This permits a greater useable power for the Fieldbus trunk; particularly if the less sensitive gas group IIB (Ethylene) is declared by use of a constant current power supply, its application into Zone 0 is not allowed 17.5 Trapezoidal V Resistive I 9 380 Fieldbus FISCO in North America The use of active semiconductors to limit the current results in power supplies being restricted to ‘ib’ level of protection in accordance with IEC & CENELEC apparatus standards ie, system is not directly applicable to Zone 0 applications However, the design of MTL power supplies satisfies the North American requirement for intrinsically safe apparatus for Divisions 1 & 2 10 Fieldbus The FISCO model Power Supply : constant current control : trapezoidal fall-off V max up to 17.5 volts IIC Imax 183 mA Pmax 2.56 Watts IIB 380 mA 5.32 Watts Safety Factor of 1.5 has been incorporated 17.5 Trapezoidal V Resistive I 11 380 Fieldbus Comparison of Safety Parameters FOUNDATION Fieldbus FF-816 Ci 13 FISCO Parameters FISCO IIC FISCO IIB Ui 24 Volts 17.5 Volts 17.5 Volts Ii 250 mA 183 mA 380 mA Pi 1.2 watts 2.56 watts 5.32 watts Ci 5 nF 5 nF 5 nF Li 20 uH 10 uH 10 uH Fieldbus 14 The FISCO model The FISCO model is based on the following mandate : Each segment has only one source of power & no additional power is fed to the bus the field devices act as passive current sinks Passive line termination is in place at both ends of the main bus line Line length limited to : 1 Km in IIC : 1900 m in IIB (FF-816 limit) Spur length limited to : 30 metres (60 metres proposed) Each device : capacitance & inductance limited to Ci < 5 nF, Li < 10 uH Linear, tree, & star networks are permitted Fieldbus Documentation & Inspection Major benefits of the FISCO system are : no detailed analysis is necessary to ensure the safety of the system additions do not require reassessment of the whole system the documentation is only a list of the connected apparatus electronic format sufficient can simply cross-refer to the certification documents of the apparatus the inspection procedure is that of ensuring the system is unchanged & undamaged The reader is referred to Application Note AN9026 : Section 1.7 : Documentation & Inspection Section 8 : Certification & Safety; Documentation of FISCO Systems 17 Fieldbus FISCO - Detailed Design The calculation of how many field devices can be powered on a bus is a simple application of ‘Ohms Law’ take the current consumption of each field device, deduce the voltage drop in the trunk cable, remembering that the field devices require 9V to operate. If the assumption is : all field devices take 20mA all are located at the remote end of the IS trunk typically, the number of devices which can be powered from a IIC power supply is 5 at the end of a 600m trunk The corresponding IIB power supply will supply 13 devices at the end of a 300m trunk demonstrating the desirability of a IIB gas classification where possible 18 In practice most instruments take less than 20 mA thus permitting an increase in population Fieldbus Terminators FISCO power supplies typically contain a permanently connected terminator which defines one end of the IS trunk The field end of the IS trunk also requires to be terminated Terminators are used to present a 100 impedance to each end of the trunk to match the cable characteristic impedance to avoid reflections typical certification : ATEX Category II 1 CENELEC EEx ia IIC T4 FBT1-IS Typically, the terminator is FISCO approved, and hence can be used without any further consideration of the system safety R L C R L C R L C Terminator 100 1 F 19 Fieldbus Host Typical application L N E DC supply T T Power conditioner T Safe Area Zone 1 / Div1 Hazardous Area The Fieldbus The incoming power supply is converted to an intrinsically safe supply to feed the IS trunk 20 T signal, which is superimposed on the IS voltage, is fed via the interface device to & from the field devices Fieldbus Summary FISCO serves all gas groups & hazardous areas The number of field devices that can be connected to a fieldbus segment will be limited only by : the power available the resistivity of the cable connection The segment can be extended without the need for new calculations (within the boundaries of the FISCO model ) FISCO devices from different suppliers can be interchanged without any re-calculation 22 No System certification required Fieldbus Summary Entity Approach FISCO Application Line length limit all gases : 1.9 Km (FF-816) Max spur length : 120 m Full calculation of safety parameters Line length limit : 1 Km in IIC : 1.9 Km in IIB (FF-816) Max spur length : 30 m ( 60 m proposed ) No cable parameter considerations required Simple interchange of devices Tree Spur Daisy-chain 23 31.25 kbit/s