* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Automatic Voltage Regulator AVR PPT
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Control theory wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Potentiometer wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
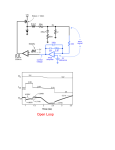
AUTOMATIC VOLTAGE REGULATOR(AVR) Automatic voltage regulator (AVR) maintains the Generator terminal voltage at a given value automatically by changing the excitation current to the Generator field. The AVR supplies the required D.C. to the Generator field depending on the load, power factor etc. to maintain a constant terminal voltage. 1 CONTROL SYSTEMS OF AVR 1. Auto control 2. Manual control 2 TYPES OF AVR 1.Single channel AVR Two controllers one is automatic and the other is manual Both the controllers are fed from the same supply 3 2. Dual channel AVR system One automatic voltage controller and one manual controller Different power supply, gate control and pulse amplifier units for each of the controllers 4 3.Twin channel AVR system Two automatic voltage regulators 5 Function of AVR compares the Generator terminal voltage with a preset reference voltage. If the Generator terminal voltage is less than the reference voltage, the AVR increases D.C. voltage across the Generator field. Maintaining the constant voltage as per the setting. 6 EXCITATION AS A CLOSED LOOP CONTROL SYSTEM If Synchronous Vg Generator Grid Excitation System The automatic voltage control system OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FEED BACK GAIN 7 I N P U T 6 2 OP AMP 3 REF OUTPUT 4 Block diagram of AVR 9 AVR inputs Generator voltage feedback signal Generator voltage reference AVR provides the following functions and signals Summing and amplification of signals to provide the exciter rectifier firing angle control signal. A signal for manual follow up. 10 AVR Action Two inputs are of opposite polarity. When the magnitudes are equal, the net input is zero. When unequal-the error is amplified and reversed to obtain a correction signal which goes to the GPG(gate pulse generator) 11 AVR CIRCUIT 12 +-50 V SUPPLY To power the regulator amplifier as well as the optional accessories such as manual follow up and power integral stabilizer 13 Regulator auxiliary card 3 phase voltage from the generator PT’s are stepped down and applied to the regulator auxiliary card which converts it to ripple free dc voltage suitable for the input of regulator amplifier. Balance Voltmeter A 30-0-30 V dc voltmeter is connected across the output of regulator amplifier to read the magnitude and polarity of the output voltage of OP-AMP at any instant. AVR Voltage Setting From the +-50 V source ,-50 V is applied and taken across a motorized potentiometer which can be operated from the control bench board. The variable output from the pot. is applied to the input of the regulator OP-AMP. Manual Voltage Control In the absence of AVR the voltage can be manually controlled. The stabilized 15 V from the MPS is applied across a second potentiometer. The variable output goes to the GPG together with output of the regulator OP-AMP. MANUAL FOLLOW UP When there is a noticeable output from the regulator OP-AMP, depending on its polarity, either of a pair of relays is automatically closed to drive the manual potentiometer motor in the required direction.