* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Animal Kingdom - Science at NESS
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
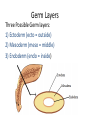
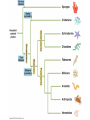
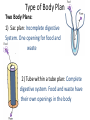
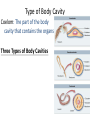
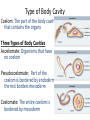
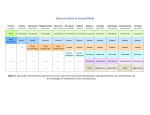
Animal Kingdom Animals Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Animalia Characteristics of the Kingdom Animalia: 1) Acquire food via ingesting food then digesting the contents (Heterotrophic) 2) Capable of movement created by muscle tissues 3) Multicellular 4) Adults are typically diploid 5) Embryo undergoes specific developmental stages 8 Phyla Phylum Members Porifera Cnidaria Platyhelminthes Nematoda Sponges Jelly fish, Sea anenome Flatworms Round worms Mollusca Annelida Echinodermata Snails, Slugs, Octopus Earthworms Starfish, Sea cucumbers Arthropoda Spiders, Crabs, Insects Chordata Sea squirts, Humans Invertebrates versus Vertebrates Endoskeleton: Bone and cartilage (human skeleton) Exoskeleton: Armour on the outside (Crab shell) Invertebrates versus Vertebrates Endoskeleton: Bone and cartilage (human skeleton) Exoskeleton: Armour on the outside (Crab shell) Invertebrates: All phyla except chordata Have exoskeletons or no skeleton at all. Vertebrates: Only in the phylum chordata Have endoskeletons. Levels of Organization Three Possible Levels of Organization: 1) cellular organization 2) Tissue organization 3) Organ organization (Not all phyla have all three) Germ Layers Three Possible Germ layers: 1) Ectoderm (ecto = outside) 2) Mesoderm (meso = middle) 3) Endoderm (endo = inside) Note: • If all 3 germ layers are present = organ level of organization jk 0 Type of Body Plan Two Body Plans: 1) Sac plan: Incomplete digestive System. One opening for food and waste 2) Tube within a tube plan: Complete digestive system. Food and waste have their own openings in the body Type of Symmetry Two Types of Symmetry: Radial: Symmetrical along the radius. If you cut the organism along its radius it will form identical parts. Bilateral: Type of Symmetry Two Types of Symmetry: Radial: Symmetrical along the radius. If you cut the organism along its radius it will form identical parts. Bilateral: (Bi = in half) If you cut the organism down the middle they will create two symmetrical halves Types of Symmetry Asymmetrical: (A = not) Does not have symmetry along any axis Segmentation Segmentation: Repeating segments found along the length of the body. Type of Body Cavity Coelom: The part of the body cavity that contains the organs Three Types of Body Cavities Type of Body Cavity Coelom: The part of the body cavity that contains the organs Three Types of Body Cavities Acoelomate: Organisms that have no coelom Pseudocoelomate: Part of the coelom is bordered by endoderm the rest borders mesoderm Coelomate: The entire coelom is bordered by mesoderm