* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Diversity II – The Evolution of Seed Plants
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
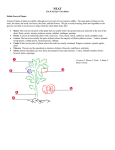
Seeds are embryos packaged with a food supply in a protective coat Reduced Gametophyte: Gametes mostly microscopic Dependent on the sporophyte for food and protection Protects anteridia and achegonia, increasing reproductive success Heterospory: Production of two types of spores Megaspores produce female gametophytes which produce the egg. Microspores produce male gametophytes which contain sperm nuclei. Ovules and Production of Eggs Megasporangium, megaspore, and the protective tissue around them make up the ovule. Ovule increases protection of the egg and the developing zygote. Increases reproductive fitness. Pollen and the Production of Sperm A Pollen grain is a male gametophyte. It contains two sperm nuclei. Has a waterproof coating, allowing for transfer by the wind. Water no longer required for sperm transfer. Seeds Have many advantages over spores. Multicellular and many layered Can provide more protection for devloping embryo Have a supply of stored energy which allows the seed to wait for good germination conditions. Stored energy is used for early growth of embryo. “Naked Seeds” means seeds are not enclosed in ovaries. Seeds are exposed on modified leaves that form cones Angiosperms (flowering plants) have seeds enclosed in fruits. Gymnosperms do not have fruits. Cycadophyta Ginkophyta Gnetophyta Coniferophyta: Largest group of gymnosperms Most are evergreen Make up large forests in Northern hemisphere at high latitudes and altitude. Includes the pines, firs, spruces, and redwoods. Flowering plants are in the phyla Anthophyta 90% of all plant species are angiosperms. Flower consists of four floral organs: Sepals - protect the flower before emergence Petals - attract pollinators Stamens - male reproductive structure produces microspores in the anthers that develop into pollen grains. Carpels - the female reproductive structure produces megaspores and their products: female gametophytes with eggs. Fruits are mature ovaries. Seeds develop from fertilized ovules. The wall of the ovary thickens to become the fruit. Fruits help disperse the seeds of angiosperms. Monocots have: One cotyledon in the seed Parallel leaf veination Flowering parts in multiples of threes Vascular bundles are scattered through out the stem. Dicots Two have: cotyledons in the seed Net leaf veination Flowering parts in multiples of fours or fives. Vascular bundles are found around edge of stem.