* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Growth and development
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Cultivated plant taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
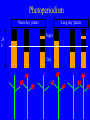
Growth and development Early experiments on bending responses to light (phototropism) led to discovery of hormones Light Control Opaque cap Tip removed Opaque collar Transparent cap Gelatin Block Mica sheet Tropisms - long term bending responses involving plant growth • • • • Phototropism - bending towards light Heliotropism - bending towards the sun Hydrotropism - bending towards water Gravitropism - bending under the influence of gravity. • Thigmotropism - bending as a response to touch Nastic movements • Short lived responses involving turgor pressure of cells • examples include leaf movements following the sun (e.g. Bean) and sensitivity to touch e.g. Mimosa Plant ‘hormones’ • Plant need to coordinate their growth and development and tune their development to that of their environment. • In order to do this, they produce chemicals which are effective at low concentration which are moved around the plant. • This definition is characteristic of animal hormones. A better phrase is Plant Growth Regulator. Auxin • Discovered as a result of work on tropisms • One main compound, Indole -3- acetic acid (IAA) • Produced in growing points (shoot and root apical meristems and young leaves) • Involved in – Cell division (with cytokinin) – Stem elongation (with Gibberellins) – Differentiation of xylem and phloem – Branching (with cytokinins) – Fruit development – Tropisms Cytokinin • Discovered by trial and error as a component of degraded DNA. • One compound Zeatin • Produced in roots • Involved in: – Cell division (with auxin) – Apical dominance (with auxin) Gibberellins • Discovered because of • Involved in: ‘foolish seedling’ – Stem elongation (with auxins) disease of rice (long, – Fruit growth (with spindly growth) auxins) caused by a fungus, – Germination Gibberella fujikori that secretes Gibberellins • Produced in growing points (shoot and root • Many gibberellins apical meristems and known (>80) young leaves) Abscisic Acid ( ABA) • Discovered because of work on leaf abscission and dormancy • One compound (ABA) • Produced all over the plant, especially in green tissues. • Involved in: – Leaf and fruit abscission – Seed dormancy – Embryo development – plant responses to water stress Ethylene • Discovered because of • Involved in: work on ripening of – Senescence fruits (Citrus and – abscission pineapple) – Fruit ripening • One compound, the gas ethylene. • Produced in all tissues, especially in response to stress. Agricultural uses of plant hormones • A knowledge of the interactions of plant hormones in plant development has resulted in many agricultural applications of plant hormones, either by their direct application, or by inhibition of their action. Agricultural uses of auxins • • • • • Hormone rooting powders Prevention of fruit drop Herbicides e.g. 2,4-D Development of seedless fruits Use in plant tissue culture for cell division, somatic embryogenesis and rooting Agricultural uses of cytokinins • Use as an ‘anti-ageing’ spray to retard senescence of cut flowers • Use in plant tissue culture for cell division, increasing branching, production of somatic embryos, and for adventitious shoots (2 routes to get a whole plant back from a single cell) Agricultural applications of Gibberellins • Dwarf plants have increased agricultural productivity • Dwarf apple by treatment with inhibitors • Enhanced stem elongation e.g. sugar cane • Production of seedless grapes. • Used to break dormancy of seeds Agricultural uses of ABA • ‘Stress hormone’ causing stomata to close under water stress • Used in plant tissue culture to ensure that somatic embryos develop normally. Agricultural uses of Ethylene • Ethylene inhibitors (e.g silver ions) used in the cut flower trade to increase shelf life. • Promotes ripening of fruits (bananas are picked green and ripen on board ship controlled by ethylene. Controlled ripening of tomatoes by use of anti-sense to ethylene • Abscission of fruits to synchronise harvesting. Circadian Rhythms • Rhythms with a cycle of about a day (exact rhythm will vary, but resynchronised every day) • Used to synchronise the plant responses to the day/night cycle and the seasons, especially flowering. Flowering • A critical daylength is often needed to induce flowering. 3 responses: – Short day. - plants will only flower when the day length is less than a certain length. – Long day - plants will only flower when the day length is more than a certain length. – Day neutral. Flower all year round. Photoperiodism ‘Short day’ plants 24 h ‘Long day’ plants Night Day Phytochrome Pr Red Pfr Far red Slow conversion in darkness