* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CommonBarberry (Berberis vulgaris L.)
Survey
Document related concepts
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
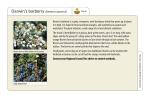
Common Barberry (Berberis vulgaris L.) Family: Berberidaceae (bear-ber-id-AYsee-ee) - From the Latinized form of the Arabic name for the Berberis genus. Alternative Pronunciation: bear-ber-id-AY-see-ay Genus: Berberis (BEAR-ber-is) –Berberis is the Latinized form of the Arabic name for the barberry fruit. Species: vulgaris (vul-gar-is) – common Common Barberry Common Barberry is an alien mediumsized thorny bush shrub which can grow up to 3 m. It grows well in dry, sunny locations. Common Barberry The leaves are shaped like a spatula. Common Barberry The pale yellow unpleasant smelling flowers appear in midspring to early summer. They hang in clusters of five or more. Common Barberry The bark is light grey to yellowish grey and yi dye which was once used in the treatment of jaundice. CommonBarberry Thorns are often in groups of three in the axils of the leaves. Common Barberry The sour tasting oblong berries are bright red and translucent. They are edible and make an excellent jelly. It once was cultivated for the fruit. Future location of photo. Host for Wheat Rust This plant was sold in nurseries but when it was discovered to be an alternate host for wheat rust fungi, which affects wheat, oats and barley, it was banned from the store shelves. Commercial production and use of the barberry was banned by the Government of Canada in 1970. Anyone having common barberry in their gardens or on their property must remove them. This plant was very rare in Altona Forest and was thought not to exist here any longer but discoveries of a number of these plants in the spring of 2006 has changed that view. It has been removed where discovered but may still exist in the forest. The Japanese barberry, which has become naturalized, is common in Altona Forest. Common Barberry 1st Nations People used Barberry to improve appetite, for treating stomach problems such as ulcers and heartburn, to reduce fever, diarrhea, indigestion, liver dysfunctiion and urinary tract diseases. More recently the active ingredients of berberine, columbamine, and oxyacanthine have shown promise in treatment of illnesses such as cholera, giardia, shigella, salmonella and E. coli infections as well as for treating liver diseases, as a stimulant for the circulatory and respiratory systems and anti-viral activities, and as a treatment for chronic candidiasis, indigestion and parasites. Japanese Barberry (Berberis thunbergii DC.) Family: Berberidaceae (bear-ber-id-AY-see-ee) – Genus: Berberis (BEAR-ber-is) – Berberis is the Arabic name for the barberry fruit. Species: thunbergii (thun-BERG-ee-eye) –Thunbergii is named for Carl Peter Thunberg (1743 – 1828). He was a Swedish botanist, student of Linnaeus, who entered the service of the Dutch East India Company as a doctor. He introduced many Japanese plants to Holland and the Western World. He became a professor of botany at Uppsala University. Japanese Barberry Other members of the family are the blue cohosh (Caulophyllum thalictroides), which flowers in terminal clusters and deeply cut leaves and the mayapple (genus Podophyllum) which has showy white flowers attached between two large palmate leaves. Japanese barberry is an invasive plant which originally came from Japan. It grows up to 1.8m but in Altona Forest is about half that size. This plant is not susceptible to the rust fungi. It is similar but a smaller shrub than the common barberry. Japanese Barberry The flowers are yellowish, about 1 cm wide, grouped in small clusters on a long pedicel. They appear from April to May. Future location of photo. Japanese Barberry The alternate, oblong, small, (1.3-3.2 cm long). simple leaves, have smooth margins and are clustered on the stems. They are bright green above, paler below. They turn a wine-colour in late Autumn. The stem is woody angled or grooved and zigzagged and reddish-brown with soft prickles or thorns which are almost 1 cm long, arranged singly at intervals along the stem. Older stems are a gray brown and finely shreddy. It grows from 90 cm to 180 cm. in dense, rounded form. The inner bark is yellow. Japanese Barberry The single small thorns are 13-15 mm long. In Altona Forest it is found along some paths in mottled sun. It might also be found in full sun to light shade. The fruit, which may persist into the winter, is a bright shiny orange-red, almost fluorescent egg-shaped berry and is usually found arising from the stem in groups of two. It is about 1 cm long and ripens in the fall. To Return to the Plant List Click on the Trout Lily Below To end this program click on this box.