* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
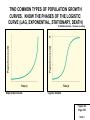
CHAPTER 8: POPULATION DYNAMICS, CARRYING CAPACITY AND CONSERVATION BIOLOGY POPULATION DYNAMICS ARE OFTEN INFLUENCED BY COMMUNITY STRUCTURE AND KEYSTONE SPECIES. THE SOUTHERN SEA OTTERS ALMOST WENT EXTINCT, AND BECAUSE OF THIS, IT WAS POSSIBLE TO GATHER DATA SUPPORTING THE HYPOTHESIS THAT THEY ARE KEYSTONE SPECIES DUE TO THEIR ROLE IN CONTROLLING SEA URCHINS BECAUSE URCHINS EAT KELP PREVENTING SEA FORESTS. Slide 1 POPULATIONS ARE DISPERSED IN 3 BASIC PATTERNS AND THIS DISPERSION IS A INTEGRAL PART OF COMMUNITY STRUCTURE. HERDS CLUMP FOR PROTECTION, CREOSOTE BUSHES PRODUCE SOIL TOXINS KEEPING NEIGHBORS AT A SET DISTANCE AND DANDELIONS DO WHAT THEY PLEASE. Figure 8-2 Page 161 Clumped (elephants) Uniform (creosote bush) Random (dandelions) Slide 2 TWO COMMON TYPES OF POPULATION GROWTH CURVES. KNOW THE PHASES OF THE LOGISTIC CURVE (LAG, EXPONENTIAL, STATIONARY, DEATH) © 2004 Brooks/Cole – Thomson Learning Population size (N) Population size (N) K Time (t) Exponential Growth Time (t) Logistic Growth Figure 8-4 Page 163 Slide 3 FOR TASMANIA 2.0 CARRYING CAPACITY Number of sheep (millions) OVERSHOOT 1.5 1.0 .5 1800 1825 1850 1875 Year 1900 1925 Figure 8-5 Page 163 Slide 4 RAINDEER INTRODUCED TO ALASKAN ISLAND (1900-50) TYPES OF POPULATION CURVES © 2004 Brooks/Cole – Thomson Learning Irregular Number of individuals Stable Cyclic Irruptive Time Slide 5 IS THIS DENSITY DEPENDENT OR DENSITY INDEPENDENT SELECTION? Density independent affect population size regardless of its numbers. Examples are floods, hurricanes, bad weather, fire habitat destruction and pesticides (agent orange). Density dependent factors have a greater effect as population density increases. Examples are competition for resources, predation, parasitism and disease (bubonic plague). Population size (thousands) 160 140 Hare 120 Lynx 100 80 60 40 20 0 1845 1855 1865 1875 1885 1895 Year 1905 1915 1925 1935 Slide 6 cockroach r-Selected Species K-Selected Species dandelion elephant Many small offspring Little or no parental care and protection of offspring Early reproductive age Most offspring die before reaching reproductive age Small adults Adapted to unstable climate and environmental conditions High population growth rate (r) Population size fluctuates wildly above and below carrying capacity (K) Generalist niche Low ability to compete Early successional species saguaro Fewer, larger offspring High parental care and protection of offspring Later reproductive age Most offspring survive to reproductive age Larger adults Adapted to stable climate and environmental conditions Lower population growth rate (r) Population size fairly stable and usually close to carrying capacity (K) Specialist niche High ability to compete Late successional species Figure 8-10 (2) PageSlide 1677 A SURVIVORSHIP CURVE SHOWS NUMBER OF SURVIVORS OF EACH AGE GROUP AND VARY BY REPRODUCTIVE TYPE. 3 TYPES. Percentage surviving (log scale) 100 10 1 0 Age Slide 8