* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Invasive Plants in Pennsylvania
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Invasive species wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
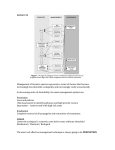
A species that arrives in a habitat it had not previously occupied Establishes a population that spreads rapidly, often at the expense of native species Throughout history of life, species have spread to new regions but human influence has increased the dispersal [1 and 2] European colonization ◦ Many species were released by the new settlers Agriculture and horticulture ◦ Many have escaped cultivation ◦ Plants were introduced as ornamentals, agricultural species, soil grasses, or soil stabilizers Accidental arrival ◦ Transport is unintentional to the area ◦ Weed seeds are accidentally harvested with commercial seeds and sown in new locations ◦ Seeds can be transported on traveler’s clothes [2] Invasive species can modify an entire ecosystem by: ◦ Shading out native species and competing for resources Approximately 42% of federally threatened and endangered plant and bird species are at risk because of invasive plants [6] ◦ Hybridizing with native species Leads to loss in genetic material ◦ Modifying nutrient regimes and flooding Reduces crop and forage quality, alters water retention [1 & 4] Invasive species can modify an entire ecosystem by: ◦ Threatening agriculture and livestock Outcompete crops for soil and water resources May poison animals ◦ Reducing recreational opportunities Swimming, boating, and fishing can be impacted [1 &4] Absence of specialized insects, diseases, and foraging animals that would naturally keep the species controlled Invasive species may be better suited to taking advantage of disturbed conditions compared to native species Invasive plants often: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Produce large numbers of new plants each season Tolerate various weather conditions Spread easily and efficiently by wind, water, and animals Grow rapidly [2 & 3] Conifer Trees - 4 species Herbs - 267 species Grasses - 67 species Hardwood Trees - 57 species Shrubs - 61 species Vines - 39 species [1] Yellow toadflax Common St. Johnswort Queen Anne's lace, wild carrot Hairy galinsoga Common velvetgrass Oxeye daisy Black medic Yellow sweetclover Timothy Buckhorn plantain [1] [8] Linaria vulgaris Yellow Toadflax [9] Hypericum perforatum Common St. Johnswort [10] Daucus carota Queen Anne's lace, wild carrot [11] Galinsoga quadriradiata Hairy galinsoga [9] [12] Holcus lanatus Common velvetgrass Chrysanthemum leucanthemum Oxeye daisy [14] [13] Medicago lupulina Black medic Melilotus officinalis Yellow sweetclover [16] Phleum pratense Timothy [15] Plantago coronopus Buckhorn plantain Prevent Eradicate ◦ More feasible if done in a restricted area ◦ Establish regular monitoring programs Control ◦ Chemical Environmentally safe herbicides ◦ Mechanical Physically remove invasive plants or change habitat conditions ◦ Biological Introduce a natural enemy Restoration ◦ Prevent reinvasion by restoring native communities [7] Overview ◦ Observe various plots of land and record how many invasive species are present and the number of each ◦ Evaluate the impact the invasive species will have in that area ◦ Create methods to reduce the number of invasive species ◦ Educate others Go back to ‘Invasive Plants of PA’ - Activity section for more information [1] USDA- Natural Resources Conservation Service. Invasive and Noxious Weeds. Assessed from: http://plants.usda.gov/java/noxious?rptType=State&statefips=42 [2] Primack, R. 2010. Essentials of Conservation Biology, 5th ed. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA. [3] The United States National Arboretum. 2009. Invasive Plants. Accessed from: http://www.usna.usda.gov/Gardens/invasives.html [4] US Fish and Wildlife Service. Volunteers and Invasive Plants. 2008. Accessed from: http://www.fws.gov/invasives/volunteersTrainingModule/nwrsystem/invasiv es.html [5] Sodhi, N. and Ehrlich, P. 2010. Conservation Biology for All. Accessed online at http://www.mongabay.com/conservation-biology-for-all.html [6] Pimentel D, Lach L, Zuniga R, Morrison D. 2005. Update on the environmental and economic costs associated alien-invasive species in the United States. Ecological Economics 52:273-288. [7] Ecological Society of America. 2004. Invasive Species. Accessed from : http://www.esa.org/education/edupdfs/invasion.pdf Images [8] http://www.invasivespeciesinfo.gov/plants/yellowtoadflax.shtml [9] http://www.fs.fed.us/r9/wildlife/nnis/herbicide_project/ [10] http://plants.usda.gov/java/profile?symbol=DACA6 [11] http://pestid.msu.edu/WeedsPlantIdentification/Hairygalinsoga/tabid/177/Default.aspx [12] http://plants.usda.gov/java/profile?symbol=HOLA&photoID=hola_006_avp.tif [13] http://plants.usda.gov/java/profile?symbol=MELU&photoID=melu_003_avp.tif [14] http://plants.usda.gov/java/profile?symbol=MEOF&photoID=meal12_1h.jpg [15] http://plants.usda.gov/java/profile?symbol=PHPR3&photoID=phpr3_002_avp.tif [16] http://plants.usda.gov/java/nameSearch