* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Population Dynamics
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Two-child policy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
The Population Bomb wikipedia , lookup
Human overpopulation wikipedia , lookup
World population wikipedia , lookup
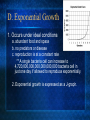
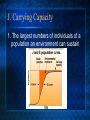
Population Dynamics The study of factors within a population that effect growth and distribution of populations. I. What is a population? A. A population is a group of the same species living in the same given area. 1. Maple Trees in a deciduous forest 2. African Elephants in a particular region of the jungle 3.Gnats in your kitchen II. Characteristics that Effect Population Dynamics A. Geographic Distribution B. Population Size and Density C. Growth Rate D. Age structure A. Geographic Distribution 1. The range a population occupies 2. Dispersion with in the range a. Clumped (humans in cities) b. Uniform (tree in an orchard) Geographical distribution of the African Elephant B. Size and Density 1. Size: The number of individuals in a population 2. Density: The number of individuals in a given area or volume such as 100 buffalo km2 100 mosquitoes m3 C. Growth Rate *Determined by... 1. number of births 2. number of deaths *Growth Rate = Births / Deaths* a. if greater then 1 then population is growing b. if less then 1 population is decreasing c. if 1 the population is in equilibrium 3. number of individuals that leave or enter the population a. immigration(enter the population) b. emigration (leave the population) D. Exponential Growth 1. Occurs under ideal conditions a. abundant food and space b. no predators or disease c. reproduction is at a constant rate ** A single bacteria cell can increase to 4,720,000,000,000,000,000,000 bacteria cell in just one day if allowed to reproduce exponentially. 2. Exponential growth is expressed as a J-graph. E. Logistic Growth 1. When a population’s growth stops or slows after exponential growth due to a. Limiting Factors: Factor that causes a population to not grow exponentially Competition Predation Parasitism/Disease Human Disturbances Drought or other climate extremes Limited Resources (nutrients, water, space…) F. Density Dependent Limiting Factor 1. effect population only after they reach a certain level 2. Effect Large Dense Populations most strongly 3. Do not effect scattered small populations as much Factors include competition predation parasitism disease G. Competition 1.Occurs among and between populations a.Mates, Space, Food, Light, Water… 2. Niche: all the biotic and abiotic resources used by and organism a. The same population occupies the same niche and therefore competes for the same resources. b. Competition between different populations results in niche overlapping. c. No two species can occupy entirely the same niche in the same place at the same time. H. Predation *Important mechanism for population control 1. Predator population directly effects and follows prey population. 2. When Predator population is down, prey is up, resulting in a rise in predator and fall in prey and the cycle continues. 3. Example: Moose/Wolves of Isle Royale I. Density Independent Factors 1. Effect all populations regardless of population size a. Unusual Weather b. Seasonal Cycles c. Certain Human Activities: Clear cutting Forests, Damming rivers, J. Carrying Capacity 1. The largest numbers of individuals of a population an environment can sustain