* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit_3_population
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
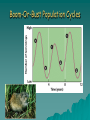
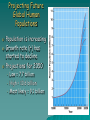
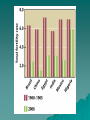
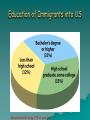
Population Change Overview of Chapter 8 o o o o o Principles of Population Ecology Reproductive Strategies The Human Population Demographics of Countries Demographics of United States Principles of Population Ecology o Population Ecology • • Study of populations and why their numbers change over time Important for • • o Endangered species Invasive species Population • Group of individuals of same species living in the same geographic area at the same time Population Density o Population density • • o The number of individuals of a species per unit area or volume at a given time Ex: minnows per Liter of pond water Ovals below have same population, and different densities Change in Population Size Change in Population Size Principles of Population Ecology o o How Do Populations Change in Size? Global scale: Growth rate Death rate r= b–d Birth rate *remember that when calculating growth rates you always use per 1000 individuals in the population unless specifically stated otherwise! Practice Problem: “Global Population Change” o You have a human population of 10, 000 where there are 200 births per year and 100 deaths per year. Calculate the natural growth rate of this population (Hint: remember that we always calculate per 1000…reduce!) o Use r = b – d Answer o 200/10,000 = 20/1000 = 0.02 o 100/10,000 = 10/1000 = 0.01 o R = b – d = 0.02 – 0.01 = 0.01 o More examples can be found at the end of chapter 8 or 1% per year Calculating Population Change: “Local Population” Growth rate Death rate Emigration rate r = (b – d) + (i – e) Birth rate Immigration rate Birth (b), Death (d), Immigration (i) and Emigration (e) are calculated per 1000 people Practice Calculating Local Population Growth o Calculate the growth of a population of 10, 000, that has 100 births, 50 deaths, 10 immigrants, and 100 emigrants o Use equation: r = (b - d) + ( i – e ) REDUCE! o Answer o o o o o o b =100/10,000 = 10/1000 = .010 d =50/10,000 = 5/1000 = 0.005 i =10/10,000 = 1/1000 = 0.001 e = 100/10,000 = 10/1000 = 0.01 So, r = (0.010 – 0.005) + (0.001 – 0.010) r = 0.005 – 0.009 = -0.004, or -0.4% per year Maximum Population Growth o Intrinsic Rate of Growth (Biotic Potential) • • Growth rate under ideal conditions J- Shaped Curve (exponential growth) Environmental Resistance o Environmental limits (resistance) • • o Prevent indefinite reproduction Unfavorable food, water, shelter, predation, etc. Carrying Capacity (K) • • • Maximum # of individuals an environment can support Causes leveling off of exponential growth S- shaped curve of logistic population growth Population Crash o Overshooting carrying capacity can lead to population crash • Abrupt decline in population density Factors That Affect Population Size o Density Dependent Factor • • Factor whose effect on population changes as population density changes Examples: • • • • Predation Disease Competition Sometimes cause Boom-or-Bust Population Cycles Boom-Or-Bust Population Cycles Case Study- Predator Prey Dynamics on Moose and Wolf Isle Royale o As wolf population increases, moose population decreases (and vice versa) Factors That Affect Population Size o Density Independent Factors • • Factors that affects population size, but is not influenced by changes in population density Examples: • • • Killing frost Severe blizzard Fire Reproductive Strategies r-selected species k-selected species -Small body size -Small broods - Early maturity -Long life span - Short life span -Slow development - Large broods -Large body size - Little or no parental -Late reproduction care -Low reproductive rate - Probability of long term -Redwood trees and survival is low human beings - Mosquitoes and Dandelions Survivorship Some populations fit two curves o o Herring Gulls Type III (as chicks) & Type II (as adults) Human Population o Demography • o Science of population structure and growth Human Population since 1980 is Jshaped curve (exponential) Population experts believe that this graph will level out during the 21 century and represent an S-shaped curve. When this happens which individuals will be those dying and which will be those surviving??? Human Population 1 Billion 1800 2 Billion 1930 3 Billion 1960 4 Billion 1975 5 Billion 1987 6 Billion 1999 6.6 Billion 2006 Population Increase in Mexico High D.R. due to Mexican revolution Analysis: death rate declined much more than the birth rate so there was a high population growth during the 20th century Doubling Time o o o o o One Way to express population growth of a country is to determine it’s doubling time Doubling Time = The amount of time it takes for a population to double in size (assuming that it’s growth rate (r) doesn’t change) Doubling time can identify a country as highly, moderate, or less developed. The shorter the doubling time the less developed the country! Formula (simplified): TD (time double) or DT (doubling time) = 70/r Replacement Level Fertility o o o Replacement-level-fertility: The number of children that a couple must produce in order to “replace” themselves It usually given as 2.1 children The number is greater than 2 b/c some children die before they hit reproductive age Total Fertility Level (global) o o o Total-Fertility-Level: The global average number of children born to each woman Currently we are at 2.8! This is way above the replacement level fertility rate! Projecting Future Global Human Populations o o o Population is increasing Growth rate (r) has started to decline Projections for 2050 • • • Low = 7.7 billion High = 10.6 billion Most likely = 9.1 billion Demographics of Countries Demographic Stages o Pre-industrial Stage • • o Transitional Stage • • o Lowered death rate Rapid population growth Industrial Stage • • o Birth and death rates high Modest population growth Birth rate decline Population growth slow Post Industrial Stage • • Low birth and death rates Population growth very slow Demographic Stages Age Structure Diagrams (or Pyramids) Explained o o o A countries age structure helps us predict the future growth of a country The number of males/females at each age from birth to death is represented It is especially important to look at the pre-reproductive and reproductive years (generally speaking if they are larger then the population is expanding Age Structure Diagrams o The number and proportion of people at each age in a population Demographics of Specific Countries World-wide Population Statistics o o o 29% of human population is under age 15 The higher the % the higher the likelihood of growth Could cause large increase in birth rates Education of Immigrants into US See envirobrief on pg. 179 of your text Addressing Population Issues Women in Egypt learning about family planning. Egypts TFR’s declined to 3.5, which was at 7.0 in the 1960’s Overview o Population and Quality of Life • • o Reducing the Total Fertility Rate • • • o Culture and Fertility Social and Economic Status of Women Family Planning Services Government Policies and Fertility • o Population and Chronic Hunger Economic Effects of Population Growth China, India, Mexico, Nigeria, Europe Achieving Population Stabilization Population and Quality of Life o o Difficult to meet basic needs in developing countries Problems associated with overpopulation: • • • • • • Environmental degradation Hunger Persistent poverty Economic stagnation Urban deterioration Health issues Carrying Capacity o Carrying Capacity (K) • o o The maximum number of individuals of a given species that a particular environment can support for an indefinite period, assuming no changes in the environment Overuse of land can cause a decrease in carrying capacity Uncertain what the carrying capacity of the earth is for humans Population and Chronic Hunger o Food security • o Condition in which people live with chronic hunger and malnutrition Effects of Chronic Hunger • • Weakened immune system Increased susceptibility to illness and disease such as • • • • Malaria Measles Diarrhea Acute respiratory illness Population and Chronic Hunger o Ways to Help Solve the Food Problem • • • Control population growth Promote economic development of developing countries without adequate food supplies Provide access to food and land resources to those who live in areas without them Areas with Greatest Food Problems Economic Effects of Population Growth o Two viewpoints from economists: • • o o Population growth stimulates economic development and technological innovation Rapidly expanding hampers developmental efforts Most observations support the second viewpoint Developmental efforts are also hampered by debt from past development attempts Reducing the Total Fertility Rate Three major influences on total fertility rate 1. Cultural traditions 2. Social & economic status of women 3. Family planning (or the lack of) Cultural Traditions o o o Culture influences and controls individuals’ behaviors Marriage age Couple is expected to have large number of children • o Children often work in family business • o Due to high infant and child mortality rates Provide support for aging parents Religious values Social & Economic Status of Women o o Gender inequality is common worldwide Disparities • • • • • • • Political participation Social status Economic status Health status Legal rights Education Employment and earnings Illiteracy in 2002 Single most important factor affecting high total fertility rates is low status of women Educational Opportunities and Fertility o Women with more education • • Marry later Have fewer children Family Planning Services o o In many countries men make reproductive decisions regarding contraceptives Family planning services offer information to both men and women on: • • • • Sexuality Contraception STDs Parenting Contraceptive Use Among Married Women of Reproductive Age Government Policies and FertilityChina o o Largest population in the world Controversial Family Planning Policy • • 1971- Chinese Government pursued birth control seriously 1979- Incentives to promote later marriages and one-child families • • Medical care, schooling for child, preferential housing, retirement funds Brought about rapid and drastic decrease in fertility Government Policies and FertilityChina o Law – controversial and unpopular • • • Compromised freedom of choice Social pressure to abort a second child Pressure to abort/kill female first child • o More boys than girls in China Law more relaxed in rural China Government Policy and Fertility- India o Severe population pressure • 1950- first country with governmentsponsored family planning • • 1976- introduced incentives and compulsory sterilization • • Did not work due to language/cultural barriers Unpopular and failure Recent years- government focused on education • Much more effective, but TFR still above replacement level (currently at 3.4) Government Policy and FertilityMexico o Young age structure • Huge potential for population growth: 33% of population is under age 15 • o Positive growth momentum 1974- government imparted educational reform, family planning, health care • Very successful Government Policy and FertilityNigeria o Population challenge • o o Largest population of any African country Very high reproductive potential: 43% of population is less than age 15 Current National Population Policy • • Improving health care Population education Government Policy and Fertility- Europe o Population concern • • o Proportion elderly people in population is increasing Due to low TFR Decrease in population could cause decrease economic growth Achieving Population Stabilization o How can developing country governments help? • • • Increase $$ allotted to pubic health and family planning services Education on affordable, safe, effective methods of birth control Increase average level of education • o Especially for women How can developed country governments help? • • Provide financial support Supporting research and development of new birth control methods