* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Primary Succession
Tropical Africa wikipedia , lookup
Reforestation wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tropical rainforest wikipedia , lookup
Ecological succession wikipedia , lookup
List of ecoregions in North America (CEC) wikipedia , lookup
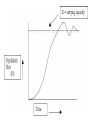
Communities, Biomes and Ecosystems with Population Dynamics Chapters 3 & 4.1 Communities • Limiting Factor: biotic or abiotic factor that restricts the members, reproduction, or distribution of an organism Most species have a range of tolerance for these factors – this plots like a bell-shaped curve Ecological Succession the changes in a community that occur over time • occurs when a new land area is exposed or when an existing land area is disturbed Primary Succession occurs on new land areas or where no soil exists – volcanic islands, bare rock, glacier melting,… Pioneer Species – the first species to inhabit an area Secondary Succession occurs when an existing community had been disturbed and regrowth occurs Succession usually culminates in a climax community. Climax Community…. •a stable community – (the living things in a given area) •is the end results of succession •the final community to inhabit an area Climax Community Desert Baja, California Latitude effects climate • Latitude = the distance of any point on Earth from the equator. • Climate is directly affected by receiving unequal solar radiation CLIMATE the average year to year conditions of temperature and precipitation in a particular region What is our climate? What is Alaska’s climate? WEATHER the day to day conditions of Earth’s atmosphere at a particular time and place What is our weather today? What about Thanksgiving Day? Greenhouse Effect occurs when heat is retained by the atmosphere • carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor and other gases in the atmosphere trap heat energy • the atmosphere acts like an insulating blanket around the planet • Can cause climate changes In summary… Latitude climate Climate weather Weather precipitation Precipitation flora (vegetation) Flora fauna (animal life) Do you see the relationship? BIOME large geographical area having… • characteristic temperature range and precipitation • characteristic plants and animals • LAND = terrestrial; WATER = aquatic Terrestrial: TUNDRA TAIGA (BOREAL FOREST, CONIFEROUS FOREST) TEMPERATE (DECIDUOUS) FOREST GRASSLAND temperate = prairie tropical = savanna DESERT TROPICAL RAIN FOREST Aquatic: MARINE FRESH Tundra • • • • • • Cold & largely treeless Covers 1/5 of world’s land Little precipitation (mostly frozen) Flora: Small, slow growing plants (grass, moss, sedge) Fauna: caribou, arctic fox, snowy owl, musk oxen Permafrost: permanently frozen layer of soil under surface • Summer can cause boggy ponds & different fauna Taiga (Boreal, Coniferous) • South of tundra • Flora: cone-bearing, evergreen trees (pines, hemlocks, spruces, junipers, firs) • Fauna: moose, grizzly bear, wolf Temperate (deciduous) forest • Trees that lose leaves found here • Warmer winter, longer summers • Flora: birch, oak, maple, beech, dogwood, & some evergreens • Fauna: fox, squirrel, WT deer, raccoon, black bear, coyote *You live here Temperate Grassland • • • • • Also known as prairies (“the bread basket”) Dominated by grasses Less rainfall, so not too many tall trees Rich, fertile soil Flora: corn, wheat, potatoes, many other cereal grains • Fauna: grazing animals (bison, other livestock) Tropical Grassland • Also called savannas • Can be in tropical or subtropical regions • Flora: Mainly grasslands with scattered trees & shrubs • Fauna: lots of herbivores (zebra, giraffe, gazelle) as well as carnivores (lions, leopards, cheetahs) Desert • Less than 25 cm rainfall per year • Can be cold as humidity is low • Sparse vegetation that have adaptations for conditions – Waxy coating, water storage, transpire @ night, thorns on exterior for protection • Flora: cacti, Joshua trees • Fauna: kit foxes, snakes, lizards, road runners Tropical Rainforest • Most productive biome • 1/5 of world’s known species live here (LOTS of insects) • Canopy: formed from a continuous layer of treetops that shades the forest floor • Fauna: sloth, birds, monkeys, beetles Aquatic/Water Ecosystems are determined by water chemistry (pH, salinity, dissolved oxygen,…) depth, flow and temperature Aquatic Ecosystems • Marine – 97.5% of water on Earth • oceans • Freshwater – 2.5% of water on Earth • Almost 69% in glaciers • Roughly 30% in groundwater • Less than 0.5% in rivers, streams, lakes, ponds, etc. *There are transitional aquatic ecosystems where marine and fresh merge wetlands, estuaries Estuary - wetlands formed where rivers (fresh water) meet salt water • Affected by the rise and fall of tides • Are usually shallow • Spawning and nursery grounds for many aquatic species Marine Ecosystems 1. Intertidal zone: periodic exposure to air (clams, oysters) 2. Coastal ocean and coral reefs 3. Open ocean zone: pelagic zone– photic (light) and aphotic (no light) benthic zone-ocean bottom abyssal zone-deepest zone What types of organisms do you think would live in each zone? Freshwater Ecosystem water having a low salt concentration (usually less than 1%) Flowing Water – stream, river, creek Standing Water – lake, pond Lake/Pond zones • Littoral zone: shallow; sunlight can reach bottom • Limnetic zone: open water; well-lit; tons of plankton found here • Profundal zone: deepest area; colder and less oxygen NOTE: not every lake will have limnetic and profundal zones population density number of individuals in a given area populations will naturally space themselves = dispersion Factors that may affect population density • Density independent: factor that does not depend on number of organisms; usually abiotic; ex. Weather event • Density dependent: factor that does depend on number of organisms; often biotic; ex. predation, competition, parasitism, etc. Remember these interactions? More population density factors… • Immigration – movement of individuals into an area • Emigration – movement of individuals out of an area Carrying Capacity – number of individuals that can be supported by a given area Human population growth is causing… • • • • severe overcrowding in areas An increase in energy demands A need for increased food supply and waste disposal very rapid ecological change (habitat destruction, overhunting, introduction of diseases) * The population tripled from 1930-2000 and is expected to double again from 2000-2050