* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Impact on the Environment
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Conservation agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Reforestation wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the environment wikipedia , lookup
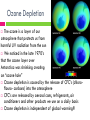
HUMAN IMPACT ON THE ENVIRONMENT Pollution Pollution is the introduction of something into the environment which has a harmful or poisonous affect. “Every year in the U.S. factories release over 3 million tons of toxic chemicals into the land, air, and water. This causes us to lose over 15 million acres of land every year.” Air Pollution Air pollution occurs when we introduce gases or particulates into the atmosphere that harm us and all other life on Earth Some different types of air pollution include: Acid Rain Greenhouse Gases Smog Ozone Depletion Air Pollution Smog is a combination of the words smoke and fog because smog is literally a smoky fog that hangs in the air. Smog is created by the burning of fossil fuels, which occurs in industrial plants, automobiles, and more. In areas where there is more industry and cars we see more smog Smog can get into peoples lungs and cause damage just like smoking would, it blocks out sunlight plants and organisms need to survive, and it causes changes in weather Land Pollution We pollute the land in many different ways: Our garbage which creates landfills Industries dump hazardous wastes Agriculture poisons the soil with pesticides, fertilizers, and other chemicals Littering kills helpless animals Land Pollution Interesting facts to think about: Every year one American produces over 3285 pounds of hazardous waste Land pollution causes us to lose 24 billion tons of top soil every year Americans generate 30 billion foam cups, 220 million tires and 1.8 billion disposable diapers every year We throw away enough trash every day to fill 63,000 garbage trucks Every day Americans throw away 1 million bushels of litter out their car window Over 80% of items in landfills can be recycled, but they’re not Land Pollution Consequences of land pollution are dire . . . Chemicals that pollute the land can lead to respiratory problems, skin irritation, birth defects, and cancer in humans and animals We are running out of space to store our garbage because it takes a very long time for certain materials to break down Land pollution can run off into lakes and rivers which will run into the oceans and start destroying aquatic ecosystems We are losing biodiversity in any ecosystem where pollution is present Water Pollution Water pollution is any chemical, physical or biological change in the quality of water that has a harmful effect on any living thing that drinks or uses or lives (in) it There are several different types of water pollutants: Disease causing agents such as bacteria, protozoa, viruses, and parasites Oxygen-demanding wastes Nitrates or phosphates Organic compounds such as oil and plastics Suspended sediment which limits light from getting through the water Radioactive compounds that can cause cancer Eutrophification Eutrophication is an increase in the organic matter in an ecosystem Eutrophication is typically caused by an increase in nitrates (from fertilizers) and Phosphates (from sewage) These are both limiting factors for plants, so when we introduce more of these substances into an ecosystem it causes excessive growth of algae As algae dies and decomposes it depletes the water of oxygen needed by other organisms living there As everything dies it builds up on the bottom causing succession of the pond into dry land to be greatly sped up Ozone Depletion The ozone is a layer of our atmosphere that protects us from harmful UV radiation from the sun We noticed in the late 1970’s that the ozone layer over Antarctica was shrinking creating an “ozone hole” Ozone depletion is caused by the release of CFC’s (chloroflouro- carbons) into the atmosphere CFC’s are released by aerosol cans, refrigerants, air conditioners and other products we use on a daily basis Ozone depletion is independent of global warming!!! Deforestation Deforestation is the removal of trees from a forest ecosystem. There are many reasons this occurs; for lumber, to make room for people to live, to create new areas for industry, and for agriculture Deforestation is causing many different problems: Habitats are being destroyed causing organisms that live there to become endangered or move into areas with people Trees absorb CO2, so when we remove them we increase greenhouse gases in the atmosphere Trees help regulate temperature of soil, without trees the soil dries out Deforestation How can we prevent this? Use methods other than clear cutting forests Require organizations to re-plant trees Preserve more forest areas What ideas do you have? Direct Harvesting Direct harvesting is the destruction of an organism, or the removal of an organism from its habitat This refers to all organisms, not just plants Examples: Organisms that are captured in distant parts of the world and sold as exotic pets (parrots or sugar gliders) Organisms that are killed for a specific body part (elephants) Now we have laws against poaching (hunting of endangered animals), but it still happens Invasive Species You might think that releasing a new species into an area that was not its original habitat would increase the biodiversity, but it actually has the opposite affect. Invasive species have no natural predators and will feed on native organisms This disrupts the food web, kills off the prey species, and creates more competition Invasive Species One of the worst things about invasive species is the techniques we have tried to use to get rid of them The most effective way to control species populations is through trapping that uses chemical scents to attract the organism We have also tried breeding and releasing predators, but that is not always successful Next Class: We’ll tackle the topics of: Global Warming and Acid Rain Ticket to Leave: Take an Exit Ticket from the computer cart and answer the following questions: One humans impact on the environment Explain what causes this problem And explain how we can help fix it Friday Bell Work Grab three or four post-it notes from the pads on the front table. On each post it write down one way humans impact the environment. ONLY ONE PER POST IT PLEASE! When you are done, stick them to the smart-board After you’ve stuck all of your post-its to the smartboard, you should quietly turn in your flower dissection lab and work on your vocabulary packet Questions? Did we come up with more positive or negative ways humans impact the environment? Why do you think this is? Why is it important to preserve the environment? What do you think will happen if we continue to destroy nature at the rate we are going? How can each person in here help to stop the negative impacts?