* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Population Biology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
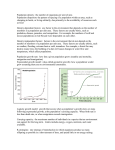
Population Biology Unit 2 Chapter 4 Population: group of same species living in a specific area This is a population of bacteria that can be studied easily in a laboratory setting. Exponential growth: as population gets larger, the growth rate becomes faster Population Growth of Houseflies Populations will continue to grow exponentially until they run out of food or space. Growth starts off slowly because there are few in the population that can reproduce. Carrying capacity The total number of organisms of one species that an environment can support indefinitely Click on image to start video. Stopping population growth When a population becomes larger than the carrying capacity, limiting factors can stop population growth. What can limit the growth of a population? Population Carrying capacity J curve S curve 0 Time FOOD PREDATORS DISEASE Exponential growth SPACE Characteristics of Population Growth Predation can affect populations. What else can affect populations? What is the relationship between predator and prey populations? Lynx and Hare Pelts Sold to the Hudson’s Bay Company Number of organisms(in thousands) Lynx Hare Times (in years) Different growth rates Some populations grow very rapidly. Why? – Ex: bacteria Different growth rates Some populations grow slowly. Why? – Ex: elephants, bears Demography study of human population size, density and distribution, movement, and its birth and death rates Birth rate is the number of live births per 1000 population in a given year. Death rate is the number of deaths per 1000 population in a given year. Calculating how fast populations grow Birthrate – Death rate = Population Growth Rate (PGR) If PGR > 0, then the population is growing. If PGR < 0, then the population is declining.