* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Populations
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
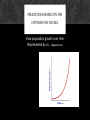
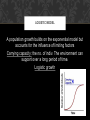
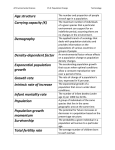
POPULATIONS Chapter 20 Lab Biology Chapter 26 Honors Biology Anticipatory Set: Count the number of dolphins in this picture… Does this represent a population of dolphins? PROPERTIES OF POPULATIONS Grp. Of organisms of the same species in a particular place at the same time. Population Size no. of individuals it contains (how do we measure it?) Population Density measures how crowded a population is (indiv. Per unit of area or volume) Dispersion spatial distribution of individuals within the population Clumped Even random POPULATION DISPERSION POPULATION DYNAMICS (CHANGE OVER TIME) Birth rate – no. of births occurring in a period of time Death rate – number of deaths in a period of time Life expectancy –how long on average an individual is expected to live Continue… Age Structure the distribution of individuals among different ages in a population Patterns of Mortality tends to conform to one of three curves on a graph called survivorship curves they show the likelihood of survival at different ages throughout the lifetime of the organism. POPULATION GROWTH RATE Growth rate the amount by which a population’s size changes in a given time This depends on 4 processes: Birth Death Emigration immigration FORMULAS FOR GROWTH RATE!! Loss… Birth rate – death rate = growth rate (per capita use 1,000) Gain… To find the no. of new indiv. That will be added to the population in a yr. Multiply the per capita growth rate by the no. of indiv. In the popul. EXPONENTIAL MODEL Exponential Model describes a population that increase rapidly after only a few generations Exponential Growth the larger the population gets the faster it grows PREDICTIONS BASED ON THE EXPONENTIAL MODEL View population growth over time Represented by a J – shaped curve LIMITATIONS OF THE EXPONENTIAL MODEL Exponential growth occurs only under rare conditions and for short periods of time Why: resource get depleted and waste builds up Limiting factor – a factor that restrains the growth of a population LOGISTIC MODEL A population growth builds on the exponential model but accounts for the influence of limiting factors Carrying capacity: the no. of indiv. The environment can support over a long period of time. Logistic growth ENVIRONMENTAL RESISTANCE Environmental resistance can be classified into two broad categories Density-independent factors Density-dependent factors POPULATION REGULATION 2 Kinds of limiting factors control population size: 1. Density-independent factors: limit populations regardless of their density Examples: climate, weather, floods, fires, pesticide use, pollutant release, and overhunting 2. Density-dependent factors: can cause birth rates to drop and/or death rates to increase Population growth slows resulting in an S-shaped growth curve (or S-curve) DENSITYINDEPENDENT FACTORS Some species have evolved means of limiting their losses Examples: seasonally migrating to a better climate or entering a period of dormancy when conditions deteriorate DENSITY-DEPENDENT FACTORS Density-dependent factors can cause birth rates to drop and/or death rates to increase Population growth slows resulting in an S-shaped growth curve (or S-curve) DENSITY-DEPENDENT FACTORS Carrying capacity is determined by the continuous availability of resources DENSITY-DEPENDENT FACTORS Include community interactions Predation Parasitism Competition HISTORY OF HUMAN POPULATION GROWTH 1. Development of Agriculture – “agricultural revolution” stabilized and increase available food supply 2. Population Explosion – 3. Population Growth today – - developed countries - developing countries