* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Indezine Template
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Human population planning wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Maximum sustainable yield wikipedia , lookup
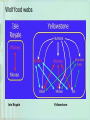
ECOLOGY ECOLOGY • Ecology – The study of the distribution and abundance of life, and the interactions between organisms and their environment. • Population ecology – the study of changes in the size and composition of populations and factors that cause those changes. Isle Royale • NW Lake Superior • ~50 miles long and ~8miles wide • Home to a population of wolves and moose (moose 90% of the wolves diet). • Longest study of any predator-prey system • Designated an International Biosphere Reserve • 99% is legally designated wilderness Isle Royale History •1900 – Moose swim 15 miles from Canada and arrive on Isle Royale. •In absence of wolves the moose were happy (see picture below). •.1929 & 1930 – Adolph Murie makes the 1st scientific observations of the Isle Royale moose, and climate. •1931 – Isle Royale became a national park as a “prime example of North Woods Wilderness.” •Early 1930s – Moose food supply dwindles as well as moose population shortly there-after. •1936 – A fire burned more than a quarter of the island •1937 – Moose population crashed •1940's – Fire stimulates growth of new browse and brood. •1948-1949 – Ice bridge forms between Canada and the island. •Late 1940s & Early 1950s – Wolves were extirpated from nearly all 48 states and migrate to Canada •Mid 1950s – A pack of Eastern timber wolves crossed over to Isle Royale. •The lives of the Isle Royale moose were never the same…… Ecology research • 1958 – Durward Allen began studying the wolves and moose of Isle Royale • 2008 – Wolves, moose, and researchers have been watching each other for 50 years. • The world's longest running wildlife research project! Isolation fosters conditions favorable for studying nature! 1. Relatively few species have colonized Isle Royale. 2. Essentially they represent a single-prey-single-predator system. • Wolves are the only predators of moose. • Moose are nearly the only prey (~10% beaver/hare) 3. Small number of species = simpler ecosystem. Wolf food webs Isle Royale Yellowstone Simplified wolf food chain Isle Royale is not too small, not too large, not too far, and not too close! If Isle Royale were... • Smaller too small to support a wolf population. • Larger too large to effectively study the moose population. • Further from the mainland wolves and moose may never have made it to island. • Closer to the mainland mainland animals would have migrated over. Studying species interactions becomes increasingly difficult with increasing species diversity. The EcoBeaker Version of Isle Royale • Model (5 species) • 3 plants • Moose • Wolves • Environment characteristics • Temperature • Seasonal changes • Plant growth Exponential Growth Model: Growth rate (r) increases with increases in population size... Assumes population increase at maximum per capita rate of growth (rmax). Instantaneous change (dN/dt) represents changes in population size with respect to time. Limitation: Applicable only to a very small population. Population size levels off at carrying capacity! Logistic Growth Model: Carrying capacity (K) - the maximum number of individuals of that species that the local environment can support at a time. Growth rate (r) decreases as the population density increases. When N = K, the population will no longer grow! Key Stone Predator Ecological Community – is a group of species that live together and interact with each other. Community Structure – the composition and relative abundance of the different types of organisms present. Keystone Predator – a predator that has an exceptionally great impact on the other species in its ecosystem relative to its abundance Intertidal Community – comprised of organisms living in the area covered by water at high tide and exposed to the air at low tide. Experiment • Simulated experiment based on 1960’s experiments conducted along the rocky shore of Washington. • You will observe which intertidal species is dominant over one another to construct a food web diagram. • Then you will remove a species and see how it influences the community. Food Chains, Food Webs and Trophic Levels Lowest Tropic Level – Producers - (algae and green plants) use energy from the sun to produce their own food Herbivores - consume producers. Higher Tropic Level – Predators eat herbivores Omnivores - take up multiple levels! Next week…… Good luck on the final! THEN…