* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Oceanic Zone
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
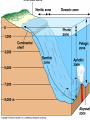
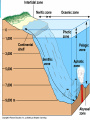
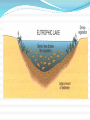
WATER! 75% of the Earth’s surface is covered with water 70% of the Earth’s surface is the ocean These aquatic ecosystems can be divided into many different types based on the salt level, locations and depth. OCEAN ZONES The zones of the ocean are determined based on: Availability of light Amount of salt (salinity) Depth of the water Aphotic zone – area where sunlight canNOT penetrate. No photosynthesis takes place here Photic zone – area where sunlight reaches, lots of photosynthesis occurs in this region, it is a few hundred meters deep The ocean can also be divided based on how close to shore and depth of water Intertidal zone – Area of shoreline that is twice daily covered by water during high tide and is exposed to air during low tide Also exposed to crashing waves Organisms that live here must be adapted to the changing conditions and have a way to deal with the force of the waves Exs: crabs, clams, mussels, starfish, sea anemones Neritic Zone – Area from end of intertidal to the edge of the continental shelf. Relatively shallow (180 meters deep) Most productive zone of the ocean – coral reefs are found here along with hundred of species Lots of nutrients and plankton are available here Exs: fish, turtles, coral, crustaceans, mollusks Oceanic Zone Deep water of open ocean Fewer species Not as many nutrients Lots of plankton ½ of the world’s photosynthesis takes place here Can be further divided PELAGIC – open ocean BENTHIC – ocean bottom, dark and cold Estuary Areas where freshwater rivers and streams flow into the ocean Ex: Chesapeake Bay Examples are mud flats, bogs, salt marsh, swamp forest Inhabitants are these areas are adapted for frequent change! Rich in species – provide areas for animals to breed, raise young and rest during migrations Estuary Estuary Estuary FRESHWATER Salt concentration of 0.005% Includes lakes, ponds, streams, rivers Types of lakes: Eutrophic – rich in organic matter/vegetation, water is murky, lots of algae growth, may use all available oxygen and cause death of many organisms Oligotrophic – little organic matter/vegetation, water is clear, bottom is sandy or rocky Eutrophic Lake Eutrophic Lake Oligotrophic Oligotrophic Rivers and Streams Freshwater that flows Organisms are adapted to currents and have various methods to hold on to rocks, shore and capture food in the flowing water Slower moving streams and rivers have more life than swiftly moving ones. WETLANDS Areas where water covers the land for part of the year 2 types Swamps – woody plants (trees/shrubs) Marshlands – nonwoody plants (cattails/grasses) Importance of Wetlands Most productive freshwater ecosystem Home to a wide variety of animals and plants Provide nesting areas for birds Many animals use them for breeding/raising young Stop for migrating birds Filter pollutants! Prevent flooding! Florida Everglades