* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biodiversity, Species Interactions, and Population Control
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Two-child policy wikipedia , lookup
The Population Bomb wikipedia , lookup
World population wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Maximum sustainable yield wikipedia , lookup
Human population planning wikipedia , lookup
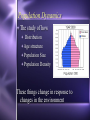
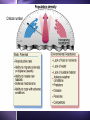
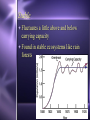
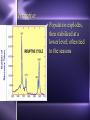
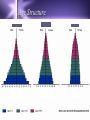
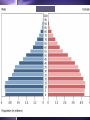
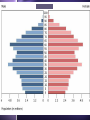
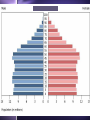
Biodiversity, Species Interactions, and Population Control Big Idea #2 Populations cannot grow indefinitely because resource are limited and there is competition for those resources Population Dynamics The study of how Distribution Age structure Population Size Population Density These things change in response to changes in the environment Some species count more than others Changes in the growth rate of Invasive species Keystone species Ecosystem engineers Has a greater impact on the biodiversity of an area than other species Distribution Population Dynamics For example: How disease affects a population How the introduction of a nonnative species affects a population How the presence of chemicals like pesticides affect populations Studying these things helps us identify keystone species Population Distribution 3 basic patterns: Clumped Uniform Random Clumped Distribution Most common in both plants and animals Why clump? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Cluster where there are resources More likely to find resources if they work together Protection from predators Teamwork to catch prey Mating group and/or help raising young Uniform Especially in plants Secrete chemicals that prevent others from growing nearby Increases chances of getting the water and soil nutrients it needs Random Pretty rare Occurs when there is no good reason for the other types Random, uniform, clumped? Why? Population Size Population Size 4 variables Birth rate (natality) + Death rate (mortality) Immigration rate + Emigration rate Let’s try some math! Biotic Potential A population’s capacity for growth under ideal conditions General rule of thumb: Big things have low biotic potential Little things have high biotic potential Blue whale & calf ants E. O. Wilson studied ants mostly Intrinsic Rate of Increase (r) The rate at which a population would grow if it had unlimited resource Species with high “r” usually: Reproduce early in life Have short generations Can reproduce often Have lots of offspring each time So what’s the difference between biotic potential and intrinsic rate of increase? Reproductive Strategies r-selected species High biotic potential Lots of offspring Little or no parental care Usually opportunist species Reproductive Strategies K-selected species Low biotic potential Few offspring Lots of parental care Usually competitive species 9 mo. Gestation, 8 years between births 22 mo. Gestation, 5 years between births Most fall somewhere in the middle Species can’t keep growing and growing… There are limiting factors that prevent this Competition for resources Predators Disease How do you feel about what you are learning? A. Happy B. Bored C. Suspicious D. Love-struck E. Confused F. Overwhelmed G. Other? _________________ Signal all that apply Population Density Population Density The number of individuals in a given volume Density-Dependent Controls • Competition for resources • Predation • Parasitism • Disease • Poisoning • Human Harvesting Density-Independent Controls • Natural disasters • Global warming • Ozone depletion Environmental Resistance The combination of all the factors that limit the growth of a population Together these factors determine the carrying capacity (K) of the population The maximum number of a species that can survive in a given area Alphabet Soup What are the letter symbols we’ve learned and what do they stand for? Genetics and Population Dynamics Genetic Diversity Difference in genes among members of a population A very important factor in the long term health and survival of a population The Founder Effect Founder Effect - a small group of individuals becomes separated from the larger population. They may have less genetic diversity than the larger population The Bottleneck Effect When only a small group survives some change in the environment Lack of variation means less adaptability Humans sometimes create bottlenecks in other species Small populations may experience genetic drift Fluctuations in gene frequencies in a small population from one generation to the next The smaller the size of the population, the more likely there is to be a major shift in allele frequencies Example If I flip a penny 100 times, how many heads should I get? If I flip a penny 10 times, would it seem really weird that I got 7 heads and only 3 tails? Why not? Inbreeding Individuals in a small population mate with each other Increase the frequency of defective genes Minimum viable population The minimum number of individuals needed to maintain a species for the long term (so no inbreeding!) How do you feel about your knowledge of genetics and population dynamics at this point? 0 – not even with prompting can I explain this topic 1 – with some prompting I could explain some of it 2 - I get the basics 3 – I understand it beyond just basic info without help 4 – I can apply what I know to a test question Population Growth Patterns Stable Fluctuates a little above and below carrying capacity Found in stable ecosystems like rain forests Irruptive Population explodes, then stabilized at a lower level; often tied to the seasons Cyclic Boom and bust; like lynx and hare - every few years/generations LE 52-18 Irregular Moose population size 2,500 Steady decline probably caused largely by wolf predation 2,000 1,500 1,000 Dramatic collapse caused by severe winter weather and food shortage, leading to starvation of more than 75% of the population 500 0 1960 1970 1980 Year 1990 2000 Age Structure Age Structure Quick Think What are the pros and cons of: Rapid population growth? No population growth? Declining population? Choose 1: Would you rather… Sleep in a bed of rats. Catch a porcupine thrown from a 2nd story window. Be sprayed by a skunk. Let a rattle snake slither across your body. Let bumble bees cover you from head to feet. Let a tarantula walk across your face. Give a speech to the student body with only your underwear on Shave off your head hair and eyebrows for the rest of the semester Stump the class • Work in teams of 2-3 • Each person write one multiple choice or short answer question on your index cards from Ch. 4 or 5 • Question on one side, answer on the other • Share your questions with your team and revise if necessary • Give your cards to Beck to share with the class