* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PHYSICS 51: Introduction
Routhian mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Hooke's law wikipedia , lookup
Old quantum theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum chaos wikipedia , lookup
Brownian motion wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
N-body problem wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
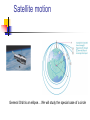
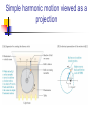
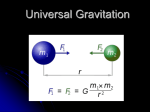
PHYSICS 50: Lecture 11.2 RICHARD CRAIG Homework #11 Chapter 12 We will skip 12.8 12.3, 12.13, 12.23, 12.54, 12.55 Due Tuesday April 22 Newton’s Law of Gravitation There is a force of attraction between any two masses F = Gm1m2/R2 G is a universal constant G = 6.67 x 10-11Nm2/kg2 For spherical shapes all the mass acts as if its at the center of the sphere (when outside the sphere) For multiple masses add the gravitational forces as vectors Escape Velocity If an object has enough kinetic energy to overcome the gravitational potential energy it can escape from the gravitational pull 1/2 mv2 > GmM/R or V > (2GM/R)1/2 Escape velocity Satellite motion General Orbit is an ellipse… We will study the special case of a circle Consider satellite orbits Condition for a circular orbit Gravitational Force = Centripetal Force GMm/R2 = mv2/R or Period of Circular orbit T = 2R3/2/(GM)1/2 Circular Orbit Examples Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Geosynchronous orbit Moon Introduction If you look to the right, you’ll see a time-lapse photograph of a simple pendulum. It’s far from simple, but it is a great example of the regular oscillatory motion we’re about to study. Describing oscillations The spring drives the glider back and forth on the air-track and you can observe the changes in the freebody diagram as the motion proceeds from –A to A and back. Simple harmonic motion Real Spring Ideal Spring (Hooke’s Law) Simple Harmonic Motion Force Equation Equation of motion (2nd order differential equation) General solution With (definition of angular frequency) SHM Solution Special case with phi = 0 Simple harmonic motion viewed as a projection