* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 8
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Hooke's law wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
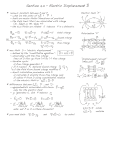
Last week … Collision means the action of bodies striking or coming together (touching). Collisions involve forces which cause is a sudden change in velocity. Collisions can be elastic, meaning they conserve energy, inelastic, meaning they do not conserve not energy, or totally inelastic (or plastic), meaning the object stick together. Work Context: Do a work out. Carrying a chair upstairs. Definition: Work = displacement * force Discussion: -Work = work done by a force on an object -Displacement = displacement of the object -Force = component of a force on the object in the direction of the displacement Discussion of work … -Lifting a 2lbs ball by 2ft: Work = 4lbs-ft -Lifting a 3kg object by 2m: Work = (weight force) * displacement = (3kg*9.8m/s2) * 2m = 58.8 kg-m/s2 = 58.8 Joule -Lowering a 3kg object by 2m: Work = (weight force) * displacement = (3kg*9.8m/s2) * (-2m) = -58.8 kg-m/s2 = -58.8 Joule - Joule is the unit of work -Pulling a heavy, but frictionless cart: Work = zero -Pulling a cart with a force of 2Newton: Work=2Newton*distance Simple Machine: An Incline Context: Humans can not produce large forces, but they can apply a small force for a long period of time. Definition: An incline is a ramp for lifting heavy objects to a given height. Discussion: -Force = Weight * height / (length of ramp) -Small slope long ramp small force -Work = Force * (length of ramp) = Weight * height An incline -Example: Lifting a 100lbs object by 1ft over a 10ft ramp force =10lbs Simple Machine: A Lever Context: Work in = Work out. The work we do on the lever is equal to the work the lever does on the object. A lever Lect. Demo: Pliers, Hydraulic Jack Definition: A lever (from French lever, "to raise", c.f. a levant) is a rigid object that is used with an appropriate fulcrum or pivot point to multiply the mechanical force that can be applied to another object. A lever has a long and a short arm. The short arm creates large forces but moves short distances. (Short arm force)*(Short arm distance) = (Long arm force)*(Long arm distance) Work in = Work out Simple Machine: A Pulley Context: Lifting heavy objects without a ramp. A pulley Definition: A pulley (also called a sheave or block) is a wheel with a groove between two flanges around its circumference. The groove normally locates a rope, cable or belt. Pulleys are used to change the direction of an applied force, or realize a mechanical advantage . Weight*lift = (pulling force)*(distance pulled) Work out = Work in Distance pulled = lift * (number of strings) Pulling force = weight / (number of strings) mechanical advantage! Work – Energy Theorem Context: Newton second law describes the effect of a force on the motion of an object: force = mass * acceleration. What is the relation between force and speed. Illustration of Work-Energy Theorem Definition: - If the total work done on some object by all forces is positive, the object speeds up. -If the total work done on some object by all forces is negative, the object slows down. Work Definition: Work = displacement * force -Work = work done by a force on an object -Displacement = displacement of the object -Force = component of a force on the object in the direction of the displacement