* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Pioneer anomaly wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
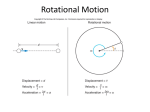
Woodward effect wikipedia , lookup
Torque wrench wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
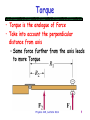
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Physics 218 Lecture 21 Dr. David Toback Physics 218, Lecture XXI 1 Checklist for Today • Things due Yesterday – Chapters 12 & 13 in WebCT • Things that are due for today – Read Chapters 14-16 • Things that are due tomorrow for Recitation – Chapter 14 problems – Read Lab hand out on webpage • Things due next Monday – Chapter 14 in WebCT Physics 218, Lecture XXI 2 The Schedule This week (4/7) • Mon: Chapter 12 & 13 material due in WebCT • Today: Reading: Chap 14-16 • Wed: Recitation on Chap 14, Lab • Thurs Lecture: Chap 15, Part 1 Next Week (4/14) • Monday: Chapter 14 due in WebCT • Tues: Exam 3 (Chaps 10-13) • Wed: Recitation on Chap 15, Lab • Thurs: Lecture on Chap 15, Part 2 Week after that (4/21) • Monday: Chapter 15 & 16 due in WebCT • Tues: Reading for Chapter 18, Lecture on Chapter 18 • Wed: Recitation on Chapter 18, Lab • Thurs: Last lecture, Chapter 18 Week after that (4/28) • No lectures or recitations Week after that (5/5) • Final: Monday May 5th, 1PM-3PM in this room Physics 218, Lecture XXI 3 Overview • Chapters 12-16 are about Rotational Motion • While we’ll do Exam 3 on Chapters 1013, we’ll do the lectures on 12-16 in six combined lectures • Give extra time after the lectures to Study for the exam • The book does the math, I’ll focus on the understanding and making the issues more intuitive Physics 218, Lecture XXI 4 Rotational Motion Chapters 12 through 16 in six combined lectures • This is the 4th of the 6 lectures • Concentrate on the relationship between linear and angular variables • Already did kinematics… Move to dynamics just like earlier this semester Physics 218, Lecture XXI 5 Angular Quantities Last time: • Position Angle q • Velocity Angular Velocity w • Acceleration Angular Acceleration a This time we’ll start by discussing the vector nature of the variables and then move forward on the others: – Force – Mass – Momentum – Energy Physics 218, Lecture XXI 6 Physics 218, Lecture XXI 7 Angular Quantities • Position Angle q • Velocity Angular Velocity w • Acceleration Angular Acceleration a Moving forward: – Force – Mass – Momentum – Energy Physics 218, Lecture XXI 8 Torque • Torque is the analogue of Force • Take into account the perpendicular distance from axis – Same force further from the axis leads to more Torque Physics 218, Lecture XXI 9 Slamming a door We know this from experience: – If we want to slam a door really hard, we grab it at the end – If we try to push in the middle, we aren’t able to make it slam nearly as hard Physics 218, Lecture XXI 10 Torque Continued • What if we change the angle at which the Force is applied? • What is the “Effective Radius?” Physics 218, Lecture XXI 11 Slamming a door We also know this from experience: – If we want to slam a door really hard, we grab it at the end and “throw” perpendicular to the hinges – If we try to pushing towards the hinges, the door won’t even close Physics 218, Lecture XXI 12 Torque • Torque is our “slamming” ability • Need some new math to do Torque Write Torque as t | t | | r || F | sin q t r F • To find the direction of the torque, wrap your fingers in the direction the torque makes the object twist Physics 218, Lecture XXI 13 Vector Cross Product C A B C A B Sin This is the last way of multiplying vectors we will see • Direction from the “right-hand rule” • Swing from A into B! Physics 218, Lecture XXI 14 Vector Cross Product Cont… Multiply out, but use the Sinq to give the magnitude, and RHR to give the direction ˆ i ˆ i 0 (sin q 0 ) ˆ i ĵ k̂ ˆ i k̂ ĵ (sin q 1 ) (sin q 1 ) Physics 218, Lecture XXI 15 Cross Product Example A AX B BX ˆ i AY ĵ ˆ i BY ĵ What is A B using Unit Vector notation? Physics 218, Lecture XXI 16 Torque and Force Torque problems are like Force problems 1. Draw a force diagram 2. Then, sum up all the torques to find the total torque Is torque a vector? Physics 218, Lecture XXI 17 Example: Composite Wheel Two forces, F1 and F2, act on different radii of a wheel, R1 and R2, at different angles 1 and 2. 1 is a right angle. If the axis is fixed, what is the net torque on the wheel? 2 F2 1 F1 Physics 218, Lecture XXI 18 Angular Quantities • Position Angle q • Velocity Angular Velocity w • Acceleration Angular Acceleration a Moving forward: – Force Torque t – Mass – Momentum – Energy Physics 218, Lecture XXI 19 Analogue of Mass The analogue of Mass is called Moment of Inertia Example: A ball of mass m moving in a circle of radius R around a point has a moment of inertia F=ma t=Ia Physics 218, Lecture XXI 20 Calculate Moment of Inertia Calculate the moment of inertia for a ball of mass m relative to the center of the circle R Physics 218, Lecture XXI 21 Moment of Inertia • To find the mass of an object, just add up all the little pieces of mass To find the moment of inertia around a point, just add up all the little moments I mr 2 or I Physics 218, Lecture XXI r dm 2 22 Torque and Moment of Inertia • Force vs. Torque F=ma t = Ia • Mass vs. Moment of Inertia m I 2 mr I or 2 r dm Physics 218, Lecture XXI 23 Pulley and Bucket A heavy pulley, with radius R, and known moment of inertia I starts at rest. We attach it to a bucket with mass m. The friction torque is tfric. Find the angular acceleration a Physics 218, Lecture XXI 24 Spherical Heavy Pulley A heavy pulley, with radius R, starts at rest. We pull on an attached rope with a constant force FT. It accelerates to an angular speed of w in time t. What is the moment of inertia of the pulley? Physics 218, Lecture XXI R 25 Less Spherical Heavy Pulley A heavy pulley, with radius R, starts at rest. We pull on an attached rope with constant force FT. It accelerates to final angular speed w in time t. A better estimate takes into account that there is friction in the system. This gives a torque (due to the axel) we’ll call this tfric. What is this better estimate of the moment of Inertia? Physics 218, Lecture XXI R 26 Next Time More on angular “Stuff” –Angular Momentum –Energy • Get caught up on your homework!!! • Mini-practice exam 3 is now available Physics 218, Lecture XXI 27 Physics 218, Lecture XXI 28 Example of Cross Product The location of a body is length r from the origin and at an angle q from the xaxis. A force F acts on the body purely in the y direction. What is the Torque on the body? z y q x Physics 218, Lecture XXI 29 Calculate Moment of Inertia 1.Calculate the moment of inertia for a ball of mass m relative to the center of the circle R 2.What about lots of points? For example a wheel Physics 218, Lecture XXI 30 Rotating Rod A uniform rod of mass m, length l, and moment of inertia I = ml2/3 rotates around a pivot. It is held horizontally and released. Find the angular acceleration a and the linear acceleration a at the end. Where, along the rod, is a = g? Physics 218, Lecture XXI 31 Two weights on a bar Find the moment of inertia for the two different Axes middle Physics 218, Lecture XXI 32 Schedule Changes Please see the handout for schedule changes New Exam 3 Date: Exam 3 Tuesday Nov. 26th Physics 218, Lecture XXI 33 Moments of Inertia Physics 218, Lecture XXI 34