* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download States of Matter
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
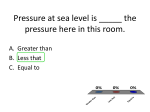
There are four states of matter… Solids Liquids Gases Plasmas Fluids are materials that Flow and have no Definite shape of their own. Pressure is a measure of how Much force is applied per Unit area. OR… F P= A The SI unit for pressure is N/m2 This is also called the Pascal (Pa). The Pascal unit is very small. It is so small that the average Air pressure here is about 1.01 X 105 Pa!! The force exerted by a gas Can be understood by using the Kinetic-Molecular Theory… This theory states that gases are Made up of very small particles; These particles are in constant Random motion; And the forces that are exerted by The particles hitting the container Are the cause of gas pressure. A woman weighs 495 N and is Wearing shoes that cover an Area of 412 cm2. What is the Average pressure that her shoes Exert on the floor? P = 1201.5 Pa A gas is very similar to a liquid. A gas has low density, Density depends on pressure, And expands to fill container The ideal gas law relates Gas volume, pressure, and Temperature. You may have seen it like This in Chemistry… PV = nRT R = proportionality constant = 0.08206 L atm K -1 mol -1 P = pressure in atm V = volume in liters n = moles T = temperature in Kelvins That formula can be rearranged To look like this… P1V1 T1 = P2V2 T2 This is most useful when Solving problems. Helium is in a container being Compressed. The initial volume, Pressure, and temp are: 15L, 2 atm, 310K. If the volume Is decreased to 12L, and the Pressure is increased to 3.5 atm, Find the final temperature. T2 = 430 K Plasma is the gas like state Of matter made up of positively Charged ions or negatively Charged electrons or a mixture Of them. This is another fluid state of matter. You have all seen plasma… Plasma exists everywhere, Stars, lightning, neon signs, etc. The main difference between a Gas and plasma is that a gas Cannot conduct electricity and A plasma can. Cohesive forces are forces Of attraction between molecules. Surface tension is a result of Cohesive forces, and is the Tendency of the surface of a Liquid to contract to the Smallest area possible. ( a sphere) Adhesion is the attractive force That acts between particles Of different substances. (like water sticking to glass) Capillary action is the rise of Water in a thin tube that occurs Because of adhesion. An ideal fluid is a fluid that has No internal friction or viscosity And is incompressible. Viscosity is the amount of “flow” a fluid has. The higher the viscosity, the Slower it flows. (thicker) So the lower the viscosity, The faster a fluid will flow. (thinner) Evaporation is the escape of particles from a liquid. This has a cooling effect. A volatile liquid that evaporates Very quickly. (many times with explosive ends) Condensation is the process Where particles return to the Liquid phase. This is due to A decrease in temperature. Pascal’s Principle states that The shape of any container has No effect on the pressure of The fluid. Or, if a pressure is created in a Closed container, it is transferred Throughout the entire container. A car weighing 1.2 X 104 N sits On a lift with an area of 0.9 m2. Compressed air exerts a force On a piston to lift the car. The Area of the piston is 0.2 m2. How Much large is the force needed To lift the car? F = 2.7 X 103 When you are swimming, you feel The pressure of the water Increase as you dive deeper. This Pressure is a result of gravity, Because of the weight of the Water above you. P = ρhg P = ρhg The pressure that a column of Water exerts on a body is equal To the density of the water times The height of the column times The acceleration due to gravity. A reservoir behind a dam is 17 m Deep. What is the pressure of the Water at the base of the dam? What is the pressure of the water 4 m from the top of the dam? The buoyant force is a force That acts upward on an object Submerged in a liquid or Floating on the liquid’s surface. It was first discovered by Archimedes. Archimedes’ principle is as follows.. Any object completely or partially Submerged in a fluid Experiences an upward buoyant Force equal in magnitude to The weight of the fluid Displaced by that object. A floating object cannot be Denser than the fluid In which it floats. A floating object’s buoyant force Is equal to the object’s weight. Fb = ρVg A cube of aluminum (1.0 X 10-3) Is submerged in water. The Density of aluminum is 2.7 X 103. What is the magnitude of the Buoyant force acting on the metal? What is the apparent weight of The block? Fb = 9.8 N Fa = 16.7 N Bernoulli’s Principle tells us That when the pressure in A fluid decreases, the Velocity increases. This is the theory that tells Us how an airplane flies. Structures & Types of Solids Crystalline Solids: highly regular arrangement of their components Such as table salt Amorphous solids: considerable disorder in their structures (glass). Most solids are much more Dense than their liquid Counterparts, water is the Exception since it is most Dense at 4 °C. This is because as a liquid Freezes its molecules fit closer together. Elasticity is the ability of a Solid object to return to its Original form after external Forces are exerted on it. If too much deformation Occurs, the object will break. Thermal expansion is the Increase in length and volume Of a material when heated. This is very common, look at a Bridge next time you drive over it, You will see metal bands there That connect the road. How big those bands are dependant On how much temperature change There is during the year. The amount of linear expansion Can be found with… ΔL = αL0ΔT α is called the average Coefficient of linear expansion. There is also area expansion… ΔA = γA0ΔT And Volume expansion… ΔV = βV0ΔT A metal bar is 2.6 m long at room Temperature, 21 °C. The bar is Put into an oven and heated to 93 °C. It is them measured and Found to be 3.4 mm longer. What is The coefficient of linear expansion Of this metal? α = 1.8 X 10-5