* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Example - mrdsample
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Hooke's law wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
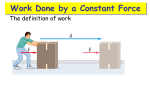
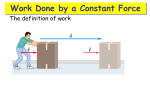
332 – UNIT 6 WORK & ENERGY Work Done by a Constant Force The definition of work, when the force is parallel to the displacement: Work for Force at an Angle If the force is at an angle to the displacement: Only the horizontal component of the force does any work (horizontal displacement). Negative, Positive, Zero Work Example: A rope inclined upward at 45o pulls a suitcase through the airport. The tension in the rope is 20N. a) How much work does the tension do, if the suitcase is pulled 100m? b) How much work does the normal force do on suitcase? c) If friction between the suitcase and floor is 9.5N, how much work is done by friction? Net Work The sum of all the work done by all forces is the net work done on an object. If the person lifts the box with the same force as gravity, the box will move at constant speed. Net work is zero. Why? Force vs Distance Graph What is the significance of this type of graph? What information can be gained from this? Find the work done on the object from 0-6.0m. Example A 3,000kg truck is to be loaded onto a ship by a crane that exerts an upward force of 31000N on the truck. This force is applied over a distance of 2.0 m. a) Find the work done on the truck by the crane. b) Find the net work done on the truck. Example 2: a) Determine the work done by gravity on a 5.0 kg block that slides down a 5.0m long ramp of angle 30o. The block starts from rest. b) If a 20N frictional force acts on the block during the entire length of the slide, determine the net work done on the block. Springs Springs can exert forces on objects. Pull on a spring, it pulls back. Push on a spring, it pushes back. Force exerted by spring is given by Hooke’s Law: Work done by spring or on spring is given by: Spring Example A 1.5kg block hangs motionless from a spring with spring constant 250 N/m. a) How far will is the spring stretched from its relaxed position? b) How much work was done in stretching the spring to its position? Question Two men, Bubba and Jerry, push against a wall. Jerry stops after 10 min, while Bubba is able to push for 5 minutes longer. Compare the work against the wall they each do. A) Bubba does 50% more work than Jerry. B) Jerry does 50% more work than Bubba. C) Bubba does 75% more work than Jerry. D) Neither of them do any work. ENERGY Kinetic Energy W-E theorem The total work done on an object is equal to its change in kinetic energy. Example You pull a sled across a frozen lake. To get started, you pull the sled (mass 80 kg) with a force of 180 N at 40° above the horizontal. The sled moves 5.0m, starting from rest. Find the final speed of your sled. Gravitational Potential Energy Elastic Potential Energy Power Example A 60kg student runs up the steps to the football stadium. The steps are 8m high. How much power was developed by the student if he reached the top of the stairs in 4.5 seconds? Example A car moves 125m in a time of 6.7s at a constant speed. If the force of air resistance was a steady 300N, find the power developed by the car during this time. Conservation of Energy Example: A child runs forward with her sled at 2.0m/s. She hops onto the sled at the top of a 5.0m high icy hill. What is her speed at the bottom? A C h B A) A 500kg rollercoaster starts from rest from a height of 20m above ground at point A. How fast will it be moving after the first drop which is 5.0m above ground at point B? Assume no friction. B) Assuming there is friction, how much energy is transferred to heat from A to C which is 12m above ground if coaster has speed of 8.5m/s at point C? The hills of a rollercoaster must get smaller than the hill that preceded it true or false Example A block (0.80 kg) is given an initial velocity of vA=1.2m/s to the right and collides with a spring of force constant k = 50.0 N/m. Determine the compression of the spring when the block is brought to rest assuming no friction. example A spring is compressed 40cm by a 0.50kg block. The spring constant is 30N/m. The surface of the ground is rough after the equilibrium point of the spring Determine how far the block will slide after it leaves the spring if µk = 0.25? How much thermal energy is generated due to friction? Question A small child slides down four frictionless sliding boards. Rank the boards in terms of which will yield the largest speed at the bottom?