* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FAD -01 Vectors
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
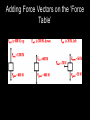
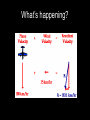
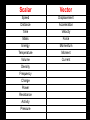
FAD -01 Vectors Vector or Scalar • A vector quantity has both direction and magnitude (size). • In contrast a scalar quantity has magnitude only We use Arrows to Draw Vectors • They have a Head and Tail How are vectors drawn? • The length of the vector arrow is used to represent its size (in this case 316N). • The direction of the arrow is measured as we would any other direction (in this case by the angle, which is 35˚ North of East) Adding Force Vectors on the ‘Force Table’ What forces are acting on the climber? Add vectors by placing them head to tail R=0 Reaction Force of rock on climber Resultant force? Gravitational pull of Earth on climber Adding Velocity Vectors in a Line Adding Velocity Vectors in a Line Some more examples Remember: the resultant vector could be negative (or in this case to the left) Resultant Vector • When we add two or more vectors, it is absolutely crucial to take the direction of the vectors into account. • The process of adding two or more vectors is known as finding the RESULTANT of the vectors. • The resultant of two or more vectors is the single vector that could replace those vectors and still have the same effect in terms of both magnitude and direction. Perpendicular Vectors • Things are slightly more complicated when vectors are not in a straight line. For example, when vectors are perpendicular to each other. Are these planes experiencing a tail wind, head wind or cross wind? tail wind, head wind or cross wind? What’s happening? Another Example What forces are acting on the climber? Pull of rope on climber Reaction force of rock on climber Gravitational pull of earth on climber The sum of these vectors is zero The man is in Equilibrium Order in which the vectors are added does not matter Horse towing a canal boat Pull of horse on boat Reaction force of water on rudder Resultant vector An imaginary vector which has the same effect as other vectors added together Regroup!! • Finalise your vector scalar groups • Copy these two groups into your notes Scalar Vector Speed Displacement Distance Acceleration Time Velocity Mass Force Energy Momentum Temperature Moment Volume Current Density Frequency Charge Power Resistance Activity Pressure Vector Addition Game Base One • Draw a route from Home Base to Base One. • Rule 1 – You can only move horizontally or vertically • Rule 2 – Each section must be a whole numbers of squares.