* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
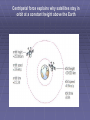
MOVING IN CIRCLES Objects will move in a straight line, at constant velocity, unless a force acts to change their speed or direction. A force at right angles to the direction of motion will make an object start to move in a circle. VELOCITY FORCE Actual curved path The force needed to move in a circle is always directed into the centre of the circle. VELOCITY FORCE We call this a CENTRIPETAL FORCE. For planets orbiting the Sun, GRAVITY provides this force. Although an object orbits at constant speed, its direction keeps changing, hence its velocity will have to change. Change of velocity is called acceleration, so this is why we require an inwards centripetal force (remember that: F = ma) NB – It accelerates but it does not get any faster!!! All objects moving in a circle have a centripetal force that keeps them changing direction constantly: Planets in orbit = GRAVITY Car going around a roundabout = FRICTION Swinging a hammer = TENSION The Centripetal force will need to be bigger if an object: Moves at a higher VELOCITY Travels in a smaller RADIUS circle/orbit Has more MASS Centripetal force explains why satellites stay in orbit at a constant height above the Earth Centripetal force also explains why planets stay in orbit at a constant distance from the Sun