* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download D - 國立東華大學
Relational algebra wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Serializability wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Ingres (database) wikipedia , lookup
Functional Database Model wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
國立東華大學試題: 資料庫管理
資訊管理學系2011.05.03
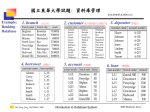
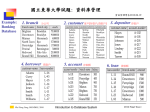
Example:
Banking
Database
1. branch
4. borrower
分公司
貸款戶
Wei-Pang Yang, IM.NDHU, 2010
2. customer 客戶(存款戶,貸款戶) 3. depositor 存款戶
5. account
存款帳
Introduction to Database System
6. loan
貸款帳
2011 Midterm Test-1
Question 1: Write SQL and Output the Results (10%)
Using the Example -- Banking Database, answering the queries:
a) Find the loan number for each loan of an amount greater than $1200
b) Find the names of all branches in the loan relations for each loan of an
amount greater than $1200, and remove duplicates.
c) How many tuples are selected from the following statement?
select
from borrower, loan
e) What is the output of the following statement?
select branch-name, avg (balance)
from account
group by branch-name
having avg (balance) > 1200
Wei-Pang Yang, IM.NDHU, 2010
Introduction to Database System
2011 Midterm Test-2
Question 2: Database System vs. File System
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
(10%)
In the early days, database applications were built on top of file
systems
Drawbacks of using file systems to store data are:
Data redundancy and inconsistency, why?
Difficulty in accessing data, why?
Integrity problems, why?
Application program unstable, why?
Database systems offer solutions to all the above problems, why?
Wei-Pang Yang, IM.NDHU, 2010
Introduction to Database System
2011 Midterm Test-3
Question 3: Answer the following Terms
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
f)
g)
h)
i)
j)
Wei-Pang Yang, IM.NDHU, 2010
(20%)
Goal of a DBMS.
Functions of a DBMS
Data Dictionary in DBMS
Schemas and Instances
Superkey
Candidate key
Three levels of an architecture for a database system
Relational-Algebra Operation: Cartesian product
Relational-Algebra Operation: Natural Join
Aggregate Functions
Introduction to Database System
2011 Midterm Test-4
Question 4: Definition of Relation
Relation:
Formally, given sets D1, D2, …. Dn
(10%)
a) Write
D1 x D2 x … x Dn = {(a1, a2, …, an)
| where each ai Di}
D1 = {
}
D2 = {
}
a Relation r is a subset of D1 x D2
x … x Dn
D3 = {
}
D1 x D2 x D3 =
Thus a relation is a set of n-tuples
(a1, a2, …, an) where
each ai Di
b) Write
account =
account
c) Why the Relation r is a subset
of D1 x D2 x … x Dn , please
explain it by using above
example.
Wei-Pang Yang, IM.NDHU, 2010
Introduction to Database System
2011 Midterm Test-5
Question 5: View
(10%)
Assume we have two queries: Q1 and Q2 as follows:
Q1.
create view big-customer as
(select account-number, branch-name
from account
where balance > 500
Q2
select *
from big-customer
a) Draw the result of Q2
b) If we want to add a new tuple to big-customer
insert into big-customer values (‘A-999’, ‘Hualien’)
Where the insertion values will be placed? Draw a table to show
your answer.
c) What are the advantages of the View?
Wei-Pang Yang, IM.NDHU, 2010
Introduction to Database System
2011 Midterm Test-6
Question 6: Using the following Example to explain the
Referential Integrity Constraint (10%)
create table account
(account-number char(10),
branch-name
char(15),
balance
integer,
primary key (account-number),
3. account
存款帳
create table depositor
(customer-name
char(20),
account-number char(10),
primary key (customer-name, account-number),
foreign key (account-number) references account,
Wei-Pang Yang, IM.NDHU, 2010
4. depositor
Introduction to Database System
references
存款
戶
2011Midterm Test-7
Question 7: Fill in the following components to the Overall
System Structure
(10%)
Query Processor
2. Storage Manager
3. Database administrator
4. Application
programmers
5. DDL interpreter
6. Compiler and Linker
7. Buffer manager
8. Data dictionary
9. Index
10. Data
11. Naïve users
12. Application programs
1.
low-level data stored
database
Wei-Pang Yang, IM.NDHU, 2010
Introduction to Database System
2011 Midterm Test-8
Question 8: Storage Management
(10%)
Storage Manager
is a program module
that provides the interface between the low-level data stored and the
application programs and queries submitted to the system.
a) What are the tasks of the Storage Manager:
Explain the following components of Storage manager:
b) Authorization and Integrity Manager
c) Transaction Manager
d) File Manager
e) Buffer manager
Wei-Pang Yang, IM.NDHU, 2010
Introduction to Database System
2011 Midterm Test-9
Question 9: multiple relations vs. Single relation (10%)
Database: A database consists of multiple relations
Information about an enterprise is broken up into parts, with each
relation storing one part of the information
E.g.: account: stores information about accounts
depositor: stores information about which customer
owns which account
customer: stores information about customers
bank
If we store all information as a single relation such as
bank(account-number, balance, customer-name, ..)
…
Question: The table bank may contain a lot of repetition of information
and null values, why?
Wei-Pang Yang, IM.NDHU, 2010
Introduction to Database System
2011 Midterm Test-10