* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IT ARCHITECTURE
Versant Object Database wikipedia , lookup
Expense and cost recovery system (ECRS) wikipedia , lookup
Data center wikipedia , lookup
Data analysis wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Information privacy law wikipedia , lookup
3D optical data storage wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
Data vault modeling wikipedia , lookup
Open data in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Business intelligence wikipedia , lookup
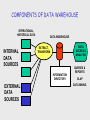
IT ARCHITECTURE © Holmes Miller 1999 BUILDING METAPHOR CUSTOMER’S CONCERN Has vision about building that will meet needs and desires ARCHITECT’S CONCERN Translates the vision into a plan to construct the building ANALOGOUS TO A BUILDING GENERAL MANAGER’S CONCERN Applications to use, data that will be accessible, and communications that will be possible IT ARCHITECT’S CONCERN Desired system functions and appropriate technology COMPONENTS Hardware Software Data Communications links HARDWARE COMPONENTS Central processing unit Primary storage Secondary storage Input devices Output devices Telecommunications links SOFTWARE COMPONENTS Operating system software Application software DATABASES Database hierarchy is: Bit Byte Field Record File Database DATABASE ORGANIZATION SEQUENTIAL ORGANIZATION Tape oriented - one file follows another DIRECT ORGANIZATION Disk oriented - can be accessed without regard to physical sequence DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS STORED IN WAY FOR DIFFERENT BUSINESSES TO ACCESS THE SAME DATA COMPONENTS Data definition language Database management software Data dictionary DATABASE TYPES HIERARCHIAL One to Many NETWORK Many to Many RELATIONAL Use Table format DATABASE PROS & CONS HIERARCHIAL High efficiency - Low flexibility NETWORK Medium efficiency - Medium flexibility RELATIONAL Low efficiency - High flexibility DATABASE TRENDS DISTRIBUTED PROCESSING Multiple systems connected via a network DISTRIBUTED DATABASE Data physically stored in more than one location DATA WAREHOUSE Consolidate current & historical information - Data Mining! DATABASE TRENDS DATA WAREHOUSE: Organization’s electronic library stores consolidated current & historic data for management reporting & analysis DATA MART: Small data warehouse for special function, e.G., Focused marketing based on customer info COMPONENTS OF DATA WAREHOUSE OPERATIONAL, HISTORICAL DATA INTERNAL DATA SOURCES DATA WAREHOUSE DATA ACCESS & ANALYSIS EXTRACT, TRANSFORM INFORMATION DIRECTORY EXTERNAL DATA SOURCES QUERIES & REPORTS OLAP DATA MINING DATABASE TRENDS ON-LINE ANALYTICAL PROCESSING (OLAP): ability to manipulate, analyze large volumes of data from multiple perspectives LINKING DATABASES TO THE WEB ELEMENTS OF DATABASE ENVIRONMENT DATA DATABASE TECHNO LOGY & MANAGEMENT ADMINISTRATION DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM DATA PLANNING & MODELING METHODOLOGY USERS COMMUNICATIONS LINKS NETWORKS Hardware and software that permits computer-computer or computer-peripheral communication COMMUNICATIONS DEVICES Hardware devices to control communication in a computer system DEVELOPING AN ARCHITECTURE SOME ISSUES On-going business process Central vs. local control Standards Vendors Rules & policies DEVELOPING AN ARCHITECTURE OVERALL PROCEDURE Where are we now? Where do we want to be? How should we get there? TWO APPROACHES Evolutionary Revolutionary DEVELOPING AN ARCHITECTURE FIVE STEPS Articulate the business strategy and architecture implications Baseline the company architecture Determine key architecture questions Design the blueprint Initiate the architecture plan UNDERSTANDING BUSINESS VALUE OF INFO SYSTEMS CAPITAL BUDGETING MODELS LIMITATIONS: Assume all relevant alternatives have been examined; cost & benefits can be expressed as $$ Ignore intangible benefits Capital Budget: Process of analyzing, selecting capital expenditures Payback method Return on investment Cost-benefit ratio Net present value Profitability index Internal rate of return Costs & Benefits: Costs: Hardware Software Services Personnel Costs & Benefits: Tangible benefit: Increased productivity Low operating costs Reduced work force Lower computer expenses Lower vendor costs Lower clerical/professional costs Reduced growth of expenses Reduced facility costs Costs & Benefits: Intangible benefit: Improved asset use; resource control; planning Increased flexibility More timely information Increased learning Attain legal requirements Enhanced employee goodwill, job satisfaction, decision making, operations Higher client satisfaction Better corporate image Portfolio Analysis: Analysis of potential applications to determine risks & benefits Determine desirable features, acceptable risks of required system Generate portfolio of characteristics, risks for each alternative Scoring model